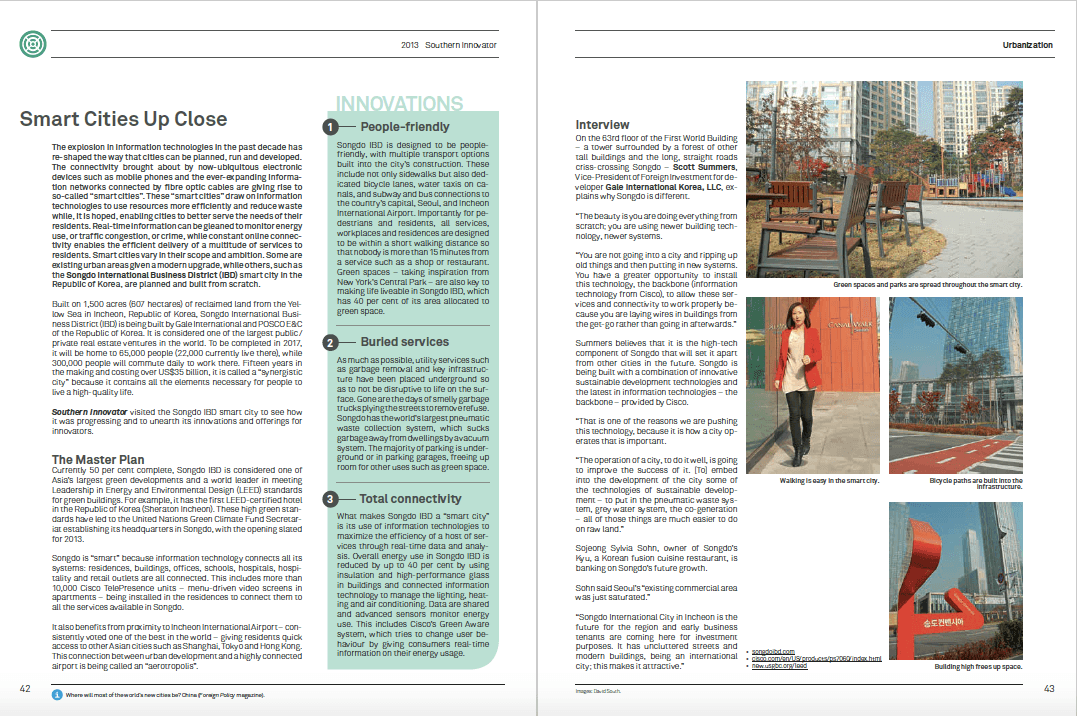
By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

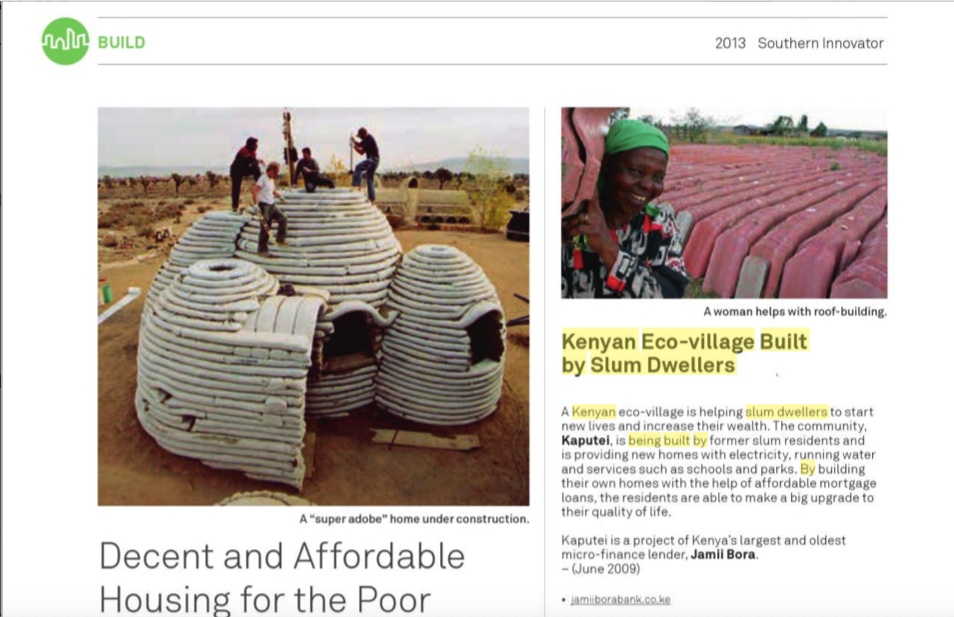
A Kenyan eco-village is helping slum dwellers to start new lives and increase their wealth. The community, Kaputei, is being built by former slum residents – some of whom used to beg to survive – and is providing new homes with electricity, running water and services like schools and parks. By building their own homes, with the help of affordable mortgage loans, the residents are able to make a big upgrade to their quality of life while acquiring real wealth.
More than 900 million people – almost a sixth of the world’s population – now live in urban slums (UN). This number will double by 2030 as a result of rapid urbanization in developing countries. Already in developing countries 43 per cent of urban dwellers live in slums, and the figure leaps to 78 per cent in the least-developed countries. The UN estimates it will take US $18 billion a year to improve living conditions for these people – and most of it will have to come from the residents themselves.
Kaputei is a project of Kenya’s largest and oldest micro-finance lender, Jamii Bora (www.jamiibora.org). Having enjoyed significant success in making loans to over 225,000 people – after starting out in 1999 with loans to just 50 beggars – it realized something on a larger scale was necessary to permanently transform the lives of poor Kenyans.
Jamii Bora’s founder, Ingrid Munro, saw the whole atmosphere of the slums as the biggest impediment to long-term life changes. “As long as you are living in the slums, you will never climb out of poverty,” she told The Independent newspaper. “Families of course need economic opportunities to rise out of poverty, but what good are they if you are still living in hell?”
Jamii Bora came up with the idea of building an entire community from scratch, and doing it in way that was affordable, ecological and sustainable, while building the wealth of the residents. Since 2007, the project has provided homes for 50 families; the target is to have homes for 2,000.
One former beggar who has built her own home is Clarice Adhiambo. An early client of Jamii Bora, she started to learn how to save, reaching her first goal of saving 1,000 Kenyan shillings (US $12.81). With Jamii Bora’s encouragement, she plowed this money back into buying some fish and selling it in the markets. Over time, she was able to grow her efforts until she was a regular market trader, and was borrowing as much as US $1,900 to fund various slum businesses.
Then came the Kaputei project. It has helped Adhiambo move from a 3 meter by 3 meter tin shack in the Nairobi slum of Soweto to her own home with running water: “So much water,” she told The Independent.
The new home is 50 square metres with two bedrooms, a sitting room and a bathroom.
Adhiambo pays US $36 a month for her mortgage — more than most people, because she wants to pay it off quickly. That compares to about US $20 a month in rent paid by many slum dwellers to live in squalor with poor services and quality of life.
Kaputei is a clever community project. Unlike attempts to build housing for the poor in isolation, Kaputei is based on neighbourhoods of 250 families each, with common community centres, playgrounds, parks and church halls. There is a town centre, and zones for commercial and industrial enterprises. The project was approved by the Kenyan government in 2004 and has planning permission for 119 hectares. Trees are being planted to provide protection from wind, add beauty, and, in time, to be a source of income or firewood. A wetland is being used to recycle waste water and is being run in partnership with Kenyan universities.
Each house costs US $1,875 to build. The homes are so cheap because the building materials are assembled in a factory on site, and the families help with the building.
Three house models are available and the families – from the Kamba, Kikuyu, Luo and Maasai peoples – choose the one they like by viewing show homes on site. Each home has access to roads, water and sewage.
It’s estimated the entire community of 2,000 families will cost US $3,750,000 for the homes, and another US $3,750,000 for infrastructure. Mortgages are offered at between 8.5 percent and 10 percent interest and are estimated to take 10 to 15 years to repay. The average mortgage is about US $32 a month.
Published: June 2009
Resources
Builders Without Borders: Is an international network of ecological builders who advocate the use of straw, earth and other local, affordable materials in construction. Website: www.builderswithoutborders.org/
World Hands Project: An NGO specialising in simple building techniques for the poor. Website:www.worldhandsproject.org
CIDEM and Ecosur specialize in building low-cost community housing using eco-materials. They have projects around the world and are based in Cuba. Website: www.ecosur.org
The Building and Social Housing Foundation: An independent research organization promoting sustainable development and innovation in housing through collaborative research and knowledge transfer. Website: www.bshf.org
Slum TV: Based deep inside Nairobi’s largest slum, Mathare, they have been seeking out the stories of hope where international media only see violence and gloom. Website: www.slum-tv.org
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/05/23/debt-free-homes-for-the-poor/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/02/17/digital-mapping-to-put-slums-on-the-map/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/04/28/envisioning-better-slums/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/16/favela-fashion-brings-women-work/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/16/housing-innovation-in-souths-urban-areas/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/04/28/innovation-in-the-slums-can-bring-peace-and-prosperity/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/31/mapping-beirut-brings-city-to-light/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/19/securing-land-rights-for-the-poor-now-reaping-rewards/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/17/tiny-homes-to-meet-global-housing-crisis/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/18/toilet-malls-make-going-better/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/17/the-water-free-south-african-bathing-solution/



https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/03/05/southern-innovator-issue-4/

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
2009: Development Challenges, South-South Solutions
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023














You must be logged in to post a comment.