“Great economic and business reporting! Very helpful for us.” Africa Renewal, Africa Section United Nations Department of Public Information
By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

Mapping to Protect Kenya’s Environment: the eMazingira Solution Development Challenges:Powerful new grassroots crowd-mapping tools have sprung up in the past few years across the global South, from Brazil’s Wikicrimes (www.wikicrimes.org) real-time crime mapping technology to the now famous Ushahidi (http://ushahidi.com) – a non-profit company making the free and open source Ushahidi software for information collection, visualization and interactive mapping – from its base in Kenya. They share some common features. All draw on the widespread use of mobile phones in the global South combined with growing access to the Internet, either through 3G mobile phone services, WiFi wireless connections, Internet centres or increasingly available broadband Internet services.
Building an Interactive Radio Network for Farmers in Nigeria Development Challenges:As solar power technology has improved, new pioneers have emerged to exploit this innovation. Several decades ago, solar power was seen as too expensive for wide-scale roll out in poor countries and communities. But today, an army of solar technology pioneers has fanned out across the world to show the new wave of innovations and how they make solar power affordable.
African Manufacturing Pioneers Proving it is Possible to Thrive Development Challenges: Africa’s paradox is that it is home to the greatest share of the world’s unexploited resources, yet has some of the world’s lowest per capita incomes. History has shown that exploiting the continent’s resources alone for export markets does little to improve incomes and living conditions in Africa, which in turn does nothing to improve human development. The key to resolving this paradox is made-in-Africa jobs, in particular high-value jobs that make products.
New African Film Proving Power of Creative Economy Development Challenges:A new movie is generating excitement around life in the war-torn, chaotic and impoverished Democratic Republic of the Congo (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Democratic_Republic_of_the_Congo) – the central African nation – and proving how versatile and resilient a creative economy can be in a crisis.
Ghana: Oil-rich City Sparks Entrepreneurs and Debate Development Challenges: Commodity booms can seem like the answer to a poor nation’s prayers, a way to fulfil all their development dreams and goals. The reality, however, is far more complex. More often than not, the discovery of resources sparks a mad scramble for profits and patronage, as politicians and politically connected elites carve out their slice of the new resource boom before anyone else.
Turning African Youth on to Technology Development Challenges: An African NGO believes the Internet is the single biggest key to rapid development in Africa – and it is working to connect youth, women and rural populations to the web, and in turn, switch them on to the vast resources stored across the world’s Internet sites.
Bringing the Invention and Innovation Mindset to Young Kenyans Development Challenges: A highly innovative new way to teach the basics of electronics, computing and technological innovation is being pioneered in the slums of Nairobi, Kenya. Driven by the desire to counter perceptions of apathy among young people, NGO Kuweni Serious is running a training course for girls aged over 8 years in some of the poorest parts of the city to turn on a new generation to the power of technology to make change.
African Youth Want to do Business in Fast-growing Economy Development Challenges: Africa’s growing economy is meeting head-on an optimistic young population keen to start businesses. At least that is what a new poll of African youth says, finding that one in five Africans between the ages of 15 and 24 without a current business wants to start one in the next 12 months.
Kenyan Safari Begins Minutes from Airport Development Challenges: Many people find the prospect of staying in airport hotels dreary at best. They tend to be located in industrial parts of cities or far from city centres. They can be surrounded by roads and highways and are built to move lots of people, not to look nice. The surrounding areas can be very common to all nations – warehouses, office parks, nondescript restaurants and hotels – and give few clues to where you are apart from the weather and the languages on the sign boards.
African Botanicals to be used to Boost Fight against Parasites Development Challenges: More than 1 billion people in the developing world currently suffer from tropical diseases, which leave a trail of disfigurement, disability and even death. Yet only 16 out of 1,393 – 0.01 percent – of new medicines marketed between 1975 and 1999 targeted tropical diseases (International Journal of Public Health).
Solar Sisters Doing it for Themselves: Tackling African Light Famine Development Challenges: A social enterprise is seeking to capture the power of the sun to bring light and economic opportunity to women in Africa. Using a direct-marketing distribution system, it sells solar lamps and lanterns to some of Africa’s remotest communities. Solar Sister (www.solarsister.org), launched in Uganda in 2010, is hoping to do for power generation what mobile phones have done for communication in Africa: make a technological leap to a model of grassroots power generation, rather than waiting for large-scale power schemes to eventually reach the poor and rural.
South Africa Innovates Healthcare with Prepay Phone Vouchers Development Challenges: Pioneers in Africa are experimenting with new ways to fund the delivery of healthcare that is affordable and sustainable and not dependent on foreign aid and donations. A South African company is prototyping the selling of pre-payment healthcare services through mobile phones with a range of vouchers that can be bought and downloaded at the tap of a keypad.
Ghana’s Funeral Economy Innovates and Exports Development Challenges: The West African nation of Ghana’s funeral economy is attracting innovation and grabbing attention outside the country. The nation’s elaborate – but expensive – funeral rituals provide craftsmen with a good income. And new products are being introduced to handle the financial consequences of this unavoidable fact of life.
Happy Nigeria: West African Nation Has Good Attitude Development Challenges: In the last 10 years, an increasing amount of attention has been paid to the concept of national happiness. The notion was first developed in the tiny Asian Kingdom of Bhutan (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bhutan), whose advocacy of ‘gross national happiness’ (http://www.grossnationalhappiness.com/) as a measure of national achievement just as important as Gross National Product (GNP), has been met with equal parts ridicule, respect and research.
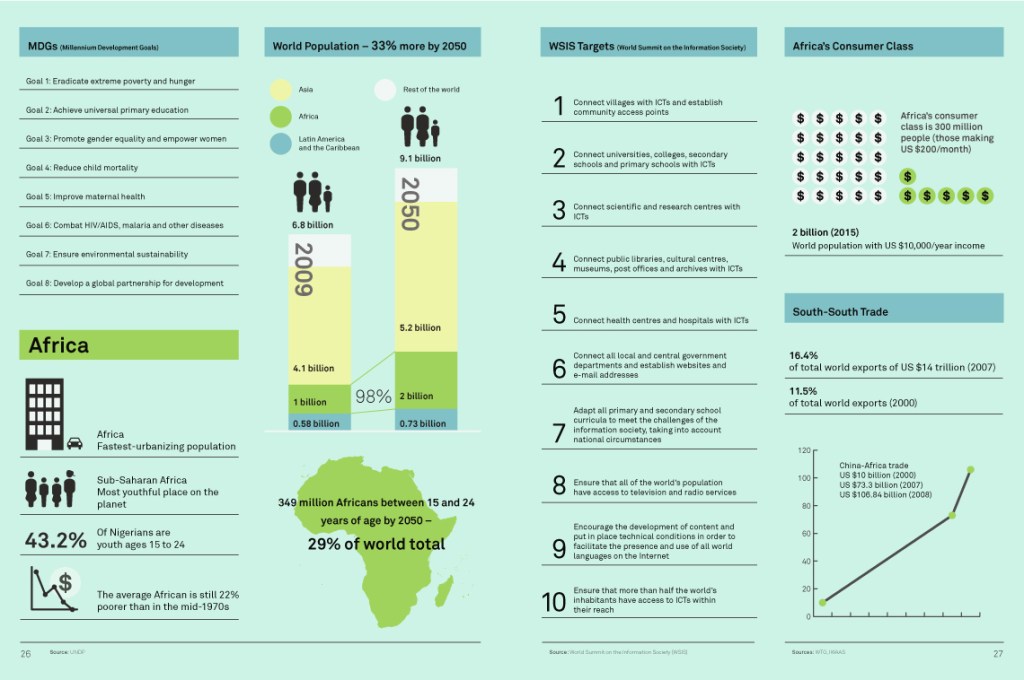
Africa’s Consumer Market in Spotlight for 2011 Development Challenges:While other parts of the world will spend 2011 worrying about their debt levels and how to spur economic growth, many factors are pointing to Africa potentially following a different story. A frenzy of activity has been building around Africa’s market opportunities and its growing middle class consumer population.
Ugandan Fish Sausages Transform Female Fortunes Development Challenges: What to do when your food production enterprise is just not making much money? It is a common problem in the global South, where farmers and fishers often struggle to survive and can face the threat of bankruptcy and destitution when trying to provide essential food for their communities.
African Supercomputers to Power Next Phase of Development Development Challenges: Information technology developments in Africa have long lagged behind those in other parts of the world. But the transformation being brought about by the widespread adoption and use of mobile phones – each one a mini-computer – and the expansion of undersea fibre optic cable connections to Africa are creating the conditions for an exciting new phase of computing growth on the continent.
Africa to Get Own Internet Domain Development Challenges: Africa is in the midst of an Internet revolution that is set only to accelerate. The continent is one of the last places to experience the information technology revolution that has swept the world in the past two decades.
Profile of African Innovators Continues to Rise Development Challenges: A mix of developments is proving that African innovators no longer need to see themselves as lone operators working in isolation.
The Water-Free South African Bathing Solution Development Challenges: As the world’s population grows from its current 7 billion to a projected 9 billion in 2050 (UN), competition for access to the Earth’s resources will become fiercer. The most essential resource for life on the planet – and an increasingly precious resource – is water. Water is necessary for the very survival of humans, animals and plants, and is also used in vast quantities by industries and farms.
Mobile Phone Shopping to Create Efficient Markets across Borders Development Challenges: An anticipated game-changing revolution in African trading set for 2013 is getting one innovative business very excited.
Egyptian Youth Turns Plastic Waste into Fuel Development Challenges: The challenge of finding alternate fuel sources is capturing the imagination of innovators across the global South. As the world’s population increases – it recently reached 7 billion (UN) – and the number of people seeking a better life grows in turn, the energy demands on the planet are pushing up competition for existing conventional fuel sources.
Shopping and Flying in Africa’s Boom Towns Development Challenges: As economies across Africa grow, the continent still has a long way to go to create infrastructure to match people’s rising expectations of what a modern, prosperous life looks like.
Teenager Uses Technology to Protect Livestock from Lions Development Challenges: In Kenya, a teenage Maasai (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maasai_people) inventor has developed a way to chase lions away from livestock that doesn’t harm the lions. It is a common practice to kill lions when they threaten or kill livestock, and this has led to a precipitous drop in the local lion population at Nairobi National Park (http://www.kws.org/parks/parks_reserves/NANP.html/), near the country’s capital, Nairobi. Lions are a significant tourist attraction for Kenya and the population decline is a threat to the future of the tourist industry.
African Innovation Eco-system Taking Shape Development Challenges: How to increase the rate of innovation in Africa? And specifically, innovation that actually improves people’s lives and reduces poverty. It is a hard question to answer, but some are putting in place the building blocks of a 21st century innovation culture by riding the information technology revolution as it rolls across Africa.
African Fuel Pioneer Uses Crisis to Innovate Development Challenges: Crisis, as the old saying goes, is also a window of opportunity. And there is one African entrepreneur who knows this better than most. Daniel Mugenga has been on a journey of innovation that has led him to become a pioneer in the emerging new field of algae technologies. The story of how he got there is a testament to the power of using business to both solve problems and make profits.
Turning Human Waste to Fertilizer: An African Solution Development Challenges: While South Africa has been free of the racist Apartheid regime since the mid-1990s, the expected boost to living standards for the majority black population has not been as widespread and as quick as many had expected.
East Africa to get its First Dedicated Technology City Development Challenges: An ambitious scheme is underway to create a vast technology city on the outskirts of Nairobi, Kenya.
Mauritanian Music Shop Shares Songs and Friendship Development Challenges: Around the world, traditional music stores selling vinyl records, tapes and CDs (compact discs) are closing down. Digital downloads distributed over the Internet and mobile phones make it unnecessary to build a music collection in these hard formats.
New Journal Celebrates Vibrancy of Modern Africa Development Challenges: Africa has seen huge changes to its communications and media in the past five years. The rise and rise of mobile phones, the expansion of the Internet and the explosion in African blogging and social media, on top of flourishing print and broadcast media, all bring an increasing range of options for telling African stories and increasing dialogue.
An Innovator’s ‘Big Chicken Agenda’ for Africa Development Challenges: Increasing the quantity and quality of food in Africa will be critical to improving the continent’s human development. And a key element in giving Africa a more secure food supply will be boosting science and knowledge on the continent and making sure it is focused on Africa’s needs and situation.
Kenya Turns to Geothermal Energy for Electricity and Growth Development Challenges: In an effort to diversify its power supply and meet growing electricity demand, Kenya is looking to increase its use of geothermal energy sources (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geothermal_electricity). Tapping the abundant heat and steam that lurks underground to drive electric power plants offers a sustainable and long-term source of low-cost energy.
African Afro Beats Leads New Music Wave to Europe Development Challenges: A surge in interest in African music in Britain is creating new economic opportunities for the continent’s musicians. The new sound heating up the U.K. music scene is “Afro Beats” – a high energy hybrid that mixes Western rap influences with Ghanaian and Nigerian popular music.
Venture Capital Surge in Africa to Help Businesses Development Challenges: Africa’s potential economic powerhouse lies in its small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Foreign direct investment (FDI) into Africa ebbs and flows based on the state of the global economy – and most of it is directed towards large enterprises and multinational companies.
Africa’s Tourism Sector Can Learn from Asian Experience Development Challenges: Africa continues to be seen as new territory for global tourism, yet it still is not even close to meeting its potential, according to a report by a South African think tank. In fact, many resorts and tourist areas are failing to fill up with visitors. This contrasts with the booming world tourism industry, which broke records in arrivals in 2011 (UNWTO).
African Farming Wisdom Now Scientifically Proven Development Challenges: Increasing the agricultural productivity of Africa is critical for the continent’s future development, and the world’s. Two-thirds of Africans derive their main income from agriculture, but the continent has the largest quantity of unproductive – or unused – potential agricultural land in the world.
Lagos Traffic Crunch Gets a New Solution Development Challenges: Around the world, traffic congestion is often accepted as the price paid for rapid development and a dynamic economy. But as anyone who lives in a large city knows, there comes a tipping point where the congestion begins to harm economic activity by wasting people’s time in lengthy and aggravating commuting, and leaving commuters frazzled and burned out by the whole experience.
New Kenyan Services to Innovate Mobile Health and Farming Development Challenges: Kenya is home to a vibrant innovation culture centred around mobile phones. While not all the services launched will be successful, the flurry of start-ups shows the country has the right combination of technical skills, bright ideas and cash to make a go of new services.
Baker Cookstoves – Designing for the African Customer Development Challenges: An innovative social enterprise is using design to create an energy-efficient cookstove for Kenya. By turning to an experienced Swedish architecture and design firm, the people behind the Baker cookstove wanted to make sure the stove’s design was as efficient as possible and relevant to the customers’ needs, while also making sure it is visually appealing and something a person would proudly want in their home.
Texting for Cheaper Marketplace Food with SokoText Development Challenges: An international group of graduate-social entrepreneurs from the London School of Economics (LSE) is pioneering a way to reduce food prices in Kenya using mobile phones.
Ethiopia and Djibouti Join Push to Tap Geothermal Sources for Green Energy Development Challenges: Ethiopia and Djibouti are the latest global South countries to make a significant commitment to developing geothermal energy – a green energy source that draws on the heat below the earth’s surface (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geothermal_energy) – to meet future development goals.
Ghana Wants to Tap Global Trendy Party Scene Development Challenges: Tourism is big business – and one of the most resilient parts of the global economy. Despite the international economic crisis that has wreaked havoc and increased unemployment and poverty in many countries since 2007, tourism is still going strong.
US $450 Million Pledged for Green Economy Investments at Kenyan Expo Development Challenges: Innovators working in the global green economy could benefit from over US $450 million in investment recently pledged at the UN’s Global South-South Development Expo held in Nairobi, Kenya.
African Fashion’s Growing Global Marketplace Profile Development Challenges: Tales of African global fashion successes have multiplied in the last few years. African fashion is seeing its profile rise as more and more shows and festivals boost awareness of the continent’s designs, designers and models. In turn, African fashion and design is being taken more seriously as an income and job generator, and as a sector able to weather the ups and downs of the global economy: people always need to wear clothes.
Pioneering African Airlines Help to Expand Routes Development Challenges: The last decade has seen a revolution in African air travel. The number of air routes has grown and this has paralleled the economic growth across the continent. As demand has been strong for Africa’s resources, it has also fueled a consumer boom that is benefiting an increasing number of people.
Solar-Powered Mobile Clinics to Boost Rural Healthcare in Africa Development Challenges: Around the world, innovative thinking is finding new ways of using solar power technology to bring electricity to underserved areas of the global South. Innovators are experimenting with new technologies, new business models and new ways to finance getting solar power into the hands of the poor.
More Futuristic African Cities in the Works Development Challenges: It has been well documented that China is undergoing the largest migration in human history from rural areas to cities. But this urbanization trend is occurring across the global South, including in Africa, as well. According to the UN, more than half the world’s population already lives in cities, and 70 per cent will live in urban areas by 2050. Most of the world’s population growth is concentrated in urban areas in the global South.
African Infrastructure Dreams Back on Agenda Development Challenges: Africa’s patchy infrastructure is not keeping pace with the continent’s economic growth. Satellite photos of Africa at night show a place where light is concentrated overwhelmingly in the South – primarily South Africa – and in the North, with a sprinkling of lights on the west and east coasts (http://geology.com/articles/satellite-photo-earth-at-night.shtml).
Burgeoning African E-commerce Industry Full of Opportunity Development Challenges: Africa has seen huge change since 2000 in the way people access information and do business electronically. The most championed accomplishment has been the widespread take-up of mobile phones. This has given birth to countless entrepreneurs and innovators who are using phones to help people, do business and sell goods and services.
African Innovators Celebrated in Prize Development Challenges: Innovation is increasingly being recognized as the key to tackling long-standing development problems in Africa, as well as across the developing and developed world. While it is easy to draw up a list of challenges facing the global South, it takes a special person to see not problems but solutions.
New Beer Helping to Protect Elephants Development Challenges: How to match the often conflicting goals of protecting animal habitats and supporting local economies? One clever solution may draw amusement but is actually a sharp marketing strategy to get attention for a product that is helping to preserve the elephants of Thailand’s Golden Triangle (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Golden_Triangle_(Southeast_Asia).
Solar Solution to Lack of Electricity in Africa Development Challenges: Electricity is critical to improving human development and living standards. Yet, for many in the global South, electricity is either non-existent or its provision is patchy, erratic, unreliable or expensive.
US $1 Trillion Opportunity for Africa’s Agribusinesses Says Report Development Challenges: As the world’s population continues to grow – surpassing 9 billion people by 2050, the United Nations estimates – and more and more people move to urban areas, producing enough food to feed this population will be one of the biggest economic challenges and opportunities in the global South.
Kenya Reaches Mobile Phone Banking Landmark Development Challenges: Financial transactions and banking with mobile phones have been a Kenyan success story.
Online Education Could Boost African Development Development Challenges: Education is recognized as a major catalyst for human development. During a high-level meeting on the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) (http://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/mdgoverview.html) in 2010, UNESCO – the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization – pointed out the necessity of making rapid gains in education if all the MDGs are to be achieved. The goals deadline is 2015 – just two years away.
African Digital Laser Breakthrough Promises Future Innovation Development Challenges: For decades many African countries have experienced low investment in research and development (R&D) and scientific innovation. One of the few nations to benefit from a sophisticated university network and research and development sector was South Africa. It still ranks top on the continent for funding R&D and its high number of scientific journals.
Preserving Beekeeping Livelihoods in Morocco Development Challenges: The clever combining of tourism and long-standing beekeeping skills has revived a local craft and is also helping to preserve the ecology of Morocco. Beekeeping, or apiculture (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beekeeping), has two clear benefits. Bee products, including honey, beeswax, propolis, pollen and royal jelly can be a valuable source of income. The other benefit is the critical role bees play in the ecology by pollinating flowers and plants as they go about their daily business.
A New African Beer Helps Smallholder Farmers Development Challenges: Africa’s growth in the past decade has held steady despite the trauma of the global economic crisis and the tumult of the “Arab Spring” in several countries of North Africa. African economies are growing because of a number of resilient trends. These include growing regional trade links, greater investment in infrastructure and the remarkable rise of China to become Africa’s number one trade partner, pushing the United States to second place (Technology + Policy). This has given birth to a growing consumer marketplace and consumer class – some 300 million people earning about US $200 a month (Africa Rising).
Made-in-Africa Fashion Brand Pioneers Aim for Global Success Development Challenges: African fashion brands have not always been the first place fashionistas turned to when shopping for new clothes or shoes in developed economies. While Africa has long been a source of inspiration in contemporary and traditional fashion, the continent has had a weak reputation for manufacturing and selling mass market global fashion brands.
Kenyan Book Company Brings Online Sales to East Africa Development Challenges: The Internet has revolutionized retail sales in many developed countries – and nowhere more so than for booksellers. The ability to offer an almost unlimited supply of books through a website is revolutionizing the way people shop and giving life to books long out of print or by unknown authors.
African Innovation Helps Make Banking Transactions Safer Development Challenges: As economies grow in Africa, more and more people are conducting their financial transactions electronically. This can be either through mobile phones and digital devices, or through the hole-in-the-wall of the automatic teller machine, or ATM.
New Apps Make Driving and Travelling in Egypt Easier, Safer Development Challenges: Mobile phones are ubiquitous across the global South. They have spawned whole new business opportunities and changed the way people solve problems and find solutions.
Angolan Film Grabs Attention at Film Festival Development Challenges: The power of the creative economy to transform lives, livelihoods – and perceptions – should never be underestimated. Creativity can transform the image of places and situations often seen in a negative light. A film from Angola is shining a light on the country’s music scene and showing the vitality of the nation in the wake of a long-running civil war.
Old Boats Become New Furniture in Senegal Development Challenges: Every country has its fair share of waste and the remnants of past economic activity. Old cars nobody wants, discarded tins of food, old plastic bags, spare copper wire, cast-off clothing – all can have a new life in the right hands.
3D Printing Gives Boy a New Arm in Sudan Development Challenges: 3D printing is rapidly going mainstream and is now starting to make a big impact in health care. One innovative solution is using the technology to manufacture artificial arms for amputees harmed by war in Africa.
African Hotel Boom Bringing in New Investment and Creating Jobs Development Challenges: Africa is experiencing a boom not seen for decades. The IMF forecasts economic growth in sub-Saharan Africa of 6 per cent in 2014, compared to global growth of 3.6 per cent.
The BRCK: Kenyan-Developed Solution to Boost Internet Access Development Challenges: Using the Internet in Africa has its challenges, as anyone who has worked there knows. Issues can include weak Wi-Fi signals, slow Internet service providers, electricity outages and power surges that can damage or destroy sensitive electronic devices.
Women Empowered by Fair Trade Manufacturer Development Challenges: There is sometimes a great deal of negativity surrounding the issue of manufacturing in Africa. Some claim the risks of doing business are too high or that the workers are not motivated enough. But one garment manufacturer is out to prove the skeptics wrong. It pays decent wages and gives its mostly female workforce a stake in the business in a bid to drive motivation and make it worthwhile to work hard.
Global South Trade Boosted with Increasing China-Africa Trade in 2013 Development Challenges: It was announced in January 2014 that China has surpassed the United States to become the world’s number one trading nation, as measured by the total value of exports and imports. This new economic behemoth also continued to grow its trade relationships with Africa.
“Pocket-Friendly” Solution to Help Farmers Go Organic Development Challenges: Interest in organic food and farming is high, and organics have become a growing global industry. The worldwide market for organic food grew by more than 25 per cent between 2008 and 2011, to US $63 billion, according to pro-organic group the Soil Association. That is an impressive accomplishment given the backdrop of the global economic crisis, and evidence that people value quality food, even in tough times.
Cheap Farming Kit Hopes to Help More Become Farmers Development Challenges: Food security is key to economic growth and human development. A secure and affordable food supply means people can meet their nutrition needs and direct their resources to improving other aspects of their lives, such as housing, clothing, health services or education.








This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2022











You must be logged in to post a comment.