By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

Access to adequate sanitation and toilet facilities is critical to making development gains. Yet this simple fact of life often gets overlooked, especially in fast-growing cities where populations are on the rise or in transit. Out of an estimated 2.6 billion people in the world without toilets, two-thirds are in southern and eastern Asia (World Toilet Organization).
It is easy to take toilet technology for granted in developed countries, but in the fast-growing urban world of the global South, increasing access will be the dividing line between a future of good human health and dignity, or misery and poor health. The biggest gains in human health always come about once people have access to clean water and sanitation. Yet this proven fact gets lost in many places for a wide variety of reasons.
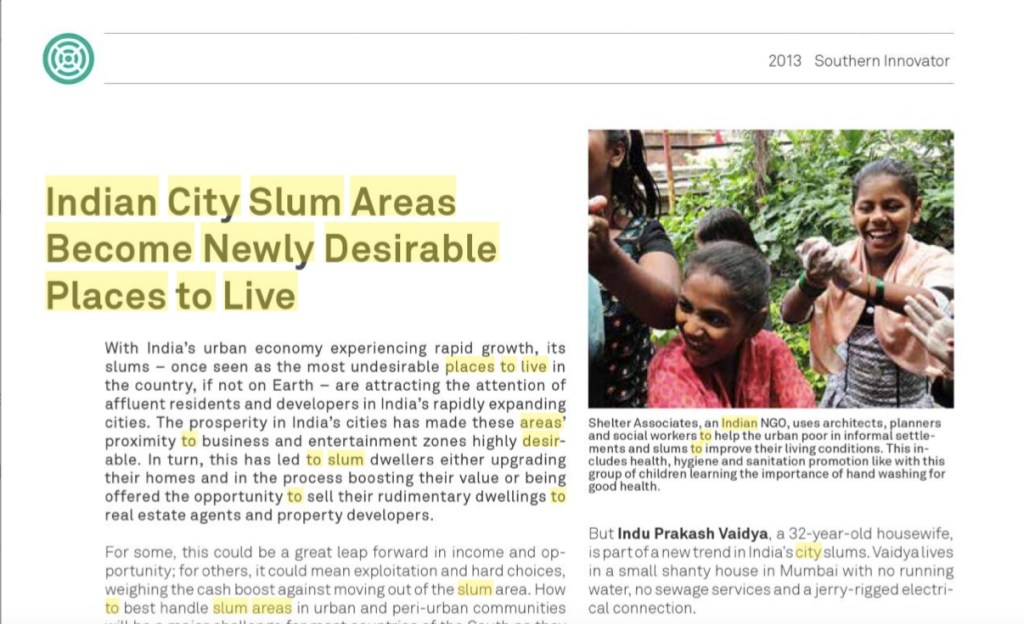
One country currently failing to meet the needs of its population is India. According to the McKinsey Global Institute, by 2030, 70 percent of India’s jobs will be created in its cities, and 590 million Indians will be city-dwellers. An enormous infrastructure task lies ahead for India: a city the size of Chicago needs to be built every year. But so far this challenge is not being met, leaving the country with the largest number of urban slum dwellers anywhere in the world. Housing is just not keeping up with populations’ needs.
As K.T. Ravindran, a professor of urban development, told the New York Times: “We require radical rethinking about urban development. It is not that there are no ideas. It is that there is no implementation of those ideas.”
It is this ability to act that makes the Sulabh International Social Service Organization stand out. The Indian non-governmental organization (NGO) sees itself as a movement and is a passionate advocate for toilets and toilet innovation for the poor and underserved.
Sulabh was founded in 1970 by Dr. Bindeshwar Pathak, who saw the vast task ahead. “I thought the challenges to provide toilet facilities have been overcome in rich countries; it has still to be met in developing countries like India,” he said.
So far, Sulabh has brought together 50,000 volunteers across the country to build toilets and sanitation facilities.
The organization’s success flows from understanding that it needs to do more than supply the ‘hardware’ of the toilets; it also needs to address the ‘software’: ideas and innovation and concepts.
The organization has directly built 1.2 million household toilets – but the government of India has built a further 54 million toilets based on the designs made by Sulabh. It’s an example of a good idea multiplying its impact when picked up by others.
While 10 million Indians use a Sulabh-built sanitation facility each day, according to the group’s website, an estimated 300 million are using a toilet based on Sulabh’s designs.
Most influential is Sulabh’s two-pit, pour-flush toilet (www.sulabhenvis.nic.in/Sulabhtechnology.htm). It consists of a toilet pan with a steep slope using gravity to flush the pan. Water is poured in to the pan to flush the toilet and the waste goes into either one of two pits. As one pit fills up with waste, waste is diverted to the second pit. After around 18 months, the first, filled pit’s waste becomes a safe, organic fertiliser suitable for agriculture and the fertiliser’s value covers the cost of emptying the pit. The successful design has been evaluated and approved by UNDP and the World Bank.
Sulabh has also been designing ways to get power and energy from toilets, building 200 biogas plants that turn the gas generated from the human excrement deposited in the toilets into a source of energy. Biogas (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biogas) is a clean-burning gas that can be made from animal, plant and human waste with the right technology and is a green solution to the need for gas to cook and run electricity generators.
Pride of place for the NGO is its vast toilet and bath complex at the holy shrine of Shri Sai Baba in Shirdi, Maharashtra (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maharashtra). Millions flock to the shrine every year, but it lacked proper sanitation facilities. To solve this problem Sulabh’s local branch has built a vast complex occupying two acres. The brightly coloured and palace-like facility has 120 toilets, 108 bathing cubicles, six dressing rooms, and urinals and can serve 30,000 people a day. There are telephones and 5,000 lockers for tourists to keep possessions safe.
There are also three biogas plants connected to the facility, generating electricity and hot water for bathing used by the toilet and bath complex. This solves the puzzle of how to fund the utilities. Water discharged from the facility is used to irrigate the surrounding green spaces.
Sulabh has also built a museum dedicated to toilets and toilet technology (http://www.sulabhtoiletmuseum.org). The museum places the toilet as a critical part of human civilisation and shows how it fits in with the cultural context of India. Toilets and toilet designs from around the world and throughout history are gathered together and make a fascinating journey through this essential human need.
Published: May 2011
Resources
1) World Toilet Organization: World Toilet Organization (WTO) is a global non- profit organization committed to improving toilet and sanitation conditions worldwide. Website: http://www.worldtoilet.org
2) World Toilet Day: On November 19 every year, this event draws attention to the lack of access for 2.6 billion people. Website: http://www.worldtoilet.org
3) Dirt: The Filthy Reality of Everyday Life: An exhibit by the prestigious Wellcome Collection on the human relationship with dirt and hygiene in history. Website:http://www.wellcomecollection.org/whats-on/exhibitions/dirt.aspx
4) World Toilet College: Established in 2005, the World Toilet College (WTC) started as a social enterprise, with the belief that there is need for an independent world body to ensure the best practices and standards in Toilet Design, Cleanliness, and Sanitation Technologies are adopted and disseminated through training. Website:http://worldtoilet.org/ourwork3.asp

Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.




This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023









You must be logged in to post a comment.