By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

Away from the news headlines, a quiet revolution has been taking place in public transportation across the global South. As cities have expanded and grown, they have also been putting in place public transport systems to help people get around and get to work.
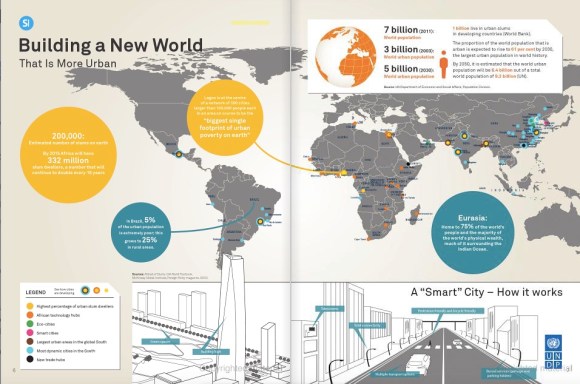
One proven, efficient way to move large numbers of people quickly through dense urban areas is to use underground subway or metro systems. Subway systems have a profound effect on local economies and wealth creation. They allow people to quickly cover distances that may once have meant hours stuck in traffic. Once people can move around a city quickly and over large distances, they can change how they work, shop, enjoy themselves. It allows people living in poor outlying neighbourhoods to travel to jobs in the city centre, improving their income prospects.
As many countries in the global South have enjoyed healthy growth rates despite the global economic crisis, and with the global financial system being flooded with stimulus funds to spur growth, the resources have become available to invest in expensive and long-term public transport solutions such as metro systems. Another factor is the scale of urbanization in the global South, which is driving governments to turn to new solutions that will help in avoiding the mistakes made in the past.
The world’s first urban underground railway system was built in 19th-century London, England. It was the product of a country that had been experiencing rapid, large-scale industrialization and urbanization unseen before in human history. Since then, the now 150-year-old London Underground (http://www.tfl.gov.uk/modalpages/2625.aspx) has acted as the arteries coursing through the city’s economic body, criss-crossing the city and delivering millions of people to work and play every day. It is now impossible to imagine Britain’s economy functioning without this efficiency tool.
Now, as the global South engages in the greatest urbanization project in human history, more cities are turning to underground metro systems to keep people, and the economy, moving. Lessons have been learned from the first generation of global South cities, which expanded rapidly in the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s. Many became quickly clogged in traffic and cloaked in pollution, and saw economic opportunity and social mobility slowed down as a consequence.
Three of the biggest metro systems in the world are now in China – Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou (The Economist). Beijing (http://www.explorebj.com/metro/) has a metro system stretching 442 kilometres and is used every day by 5.97 million people. By 2020, Beijing is hoping to boast 1,000 kilometres of metro network in the city. In Shanghai (http://www.shmetro.com/EnglishPage/EnglishPage.jsp), the 423 kilometre metro system carries 5.16 million people every day, while Guangzhou (http://www.gzmtr.com/en/) carries 4.49 million people a day.
From the 1960s, the building of metros increased around the world. More than 190 cities now have metro systems. In China, Suzhou (http://www.livingsu.com/guide_detail.asp?id=7), Kunming (http://www.urbanrail.net/as/cn/kunming/kunming.htm) and Hangzhou (http://www.urbanrail.net/as/cn/hang/hangzhou.htm) opened metro systems in 2012. Elsewhere in the global South, Lima in Peru and Algiers (http://www.metroalger-dz.com/) in Algeria recently acquired new metro systems. This means Africa now has two cities with metro systems – Algiers and Cairo in Egypt.
In India, Bangalore opened a metro system two years ago and Mumbai is close to finishing its metro. Bhopal and Jaipur also plan to build metros. In Brazil, the metros in Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro are being expanded and new systems are being built in Salvador and Cuiaba. In the Gulf states of the Middle East, Dubai (http://dubaimetro.eu/) opened a system in 2009 and Mecca (http://meccametro.com/) in Saudi Arabia in 2010. Abu Dhabi, Doha, Riyadh and Kuwait City are also working on building metro systems.
Paraguay’s capital, Asuncion, is working on one, as is Kathmandu in Nepal. Jakarta in Indonesia has attempted to build an underground metro several times and is now trying to getting one built.
But how are many of these countries funding this splurge on metro systems? According to Roland Berger Strategy Consultants (rolandberger.co.uk), global government stimulus programmes to fight the current financial crisis have increased available funding for rail systems. There are also increased resources available for transport solutions that avoid the high pollution rates that come with automobiles.
According to Mass Transit Magazine, China is using domestic consumption and increasing urbanization to spur economic growth and is hoping to increase investment in metro systems in the country by 10 per cent per year.
The target is to spend 280 billion yuan to 290 billion yuan (US $44.91 to US $46.51 billion) on metro systems in 2013, up from 260 billion yuan in 2012.
The knock-on economic boost will be felt by domestic businesses as trains and train systems are purchased. It is estimated sales of Chinese-made trains will go from 10.9 billion yuan in 2012 to 28 billion yuan by 2017.
All this new building will expand the country’s metro lines by 846 kilometres in 24 cities.
Ten Chinese cities are expecting soon to receive permission to begin work on building new metro systems: Xian, Tianjin, Chongqing, Chengdu, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Kunming, Tsingdao, Wuxi and Dongguan.
In 2013, 12 Chinese cities will complete new metro systems including Harbin, Changsha, Ningbo and Zhengzhou.
If this trend continues and expands, then the future cities of the global South could be modern, urban places that raise living standards, while avoiding damaging human health with environmental pollution and over-crowding and social exclusion.
Published: February 2013
Resources
1) Life Guangzhou: Guangzhou Awarded World’s Best Metro System. Website: http://tinyurl.com/ajdcsur
2) Inhabitat: Parisian Building Taps Metro System as a Heat Source.
Website: http://inhabitat.com/body-heat-from-paris-metro-to-heat-residential-building/
3) Digital Construction: Top Ten Metro Systems: Design and efficiency in the world of mass transit. Website:http://www.constructiondigital.com/top_ten/top-10-business/top-ten-metro-systems
4) Six of the world’s best metro systems – in pictures: A look at six metro systems around the world, from the archaeological treasures on display in Athens to the spectacular halls of Moscow’s underground system via continental Europe’s oldest network. Website:http://www.guardian.co.uk/travel/gallery/2013/jan/09/six-worlds-best-metro-systems

Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.


This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2022








You must be logged in to post a comment.