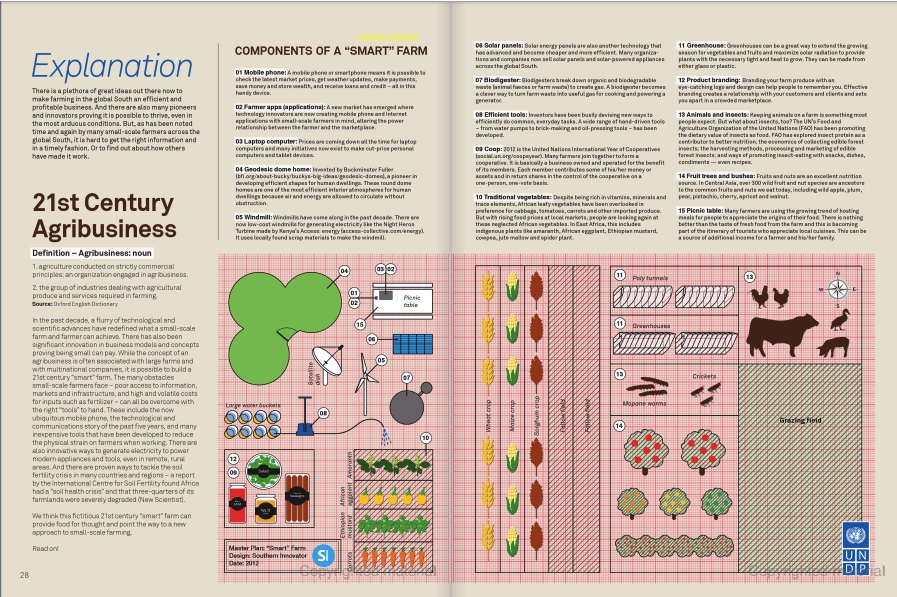
Mongolians attend for first time
By David South
UB Post (Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia), October 28, 1997
Manila, Philippines – More than 2,500 delegates have gathered in the steamy hot Philippine capital to renew the fight against HIV and AIDS.
Working up a sweat alongside other participants at the Fourth International Congress on AIDS in Asia and the Pacific are nine Mongolians – a first that isn’t going unnoticed.
The Congress opened Saturday (October 25) to the pounding beat of a theme song performed by teenagers, championing defiance of death and celebration of life.
That tone was echoed by Dr Peter Piot, executive director of UNAIDS, the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. He said the epidemic can be slowed down with the right public health measures – a positive message for Mongolia as it grapples with an STD crisis that many believe leaves the country at risk of an HIV/AIDS epidemic.
The magnitude of that epidemic outside Mongolia is startling. Around the world, 23 million people are infected with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. Between 5 and 7 million of them live in the Asia/Pacific region.
“The point is that prevention is feasible,” Piot told the Congress. “The results can be seen in those countries in the Asia-Pacific region where the epidemic has stalled or is in retreat.
“A good indicator for unsafe sexual behaviour is the STD rate. I am impressed at the sustained decline in STD rates in Australia, Hong Kong, Singapore and Thailand over the past decade.
“But I am concerned actual declines in HIV in this region have occurred only in Australia, New Zealand and Thailand.”
The countries to Mongolia’s immediate south and north are experiencing exploding health crises. In China, HIV/AIDS is increasing at a rapid rate due to factors including growing prostitution, drug use and travel – all by-products of a booming economy. The infected population is estimated at 400,000 and is expected to reach 1.2 million by the year 2000, according to China’s national AIDS committee.
To the north in Russia, a complete collapse in the public health system has dramatically slashed life expectancy and led to an upsurge in many diseases, including tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS.
With many Mongolians doing business in both these countries, there are numerous opportunities for AIDS to enter the country.
A wide range of topics is under discussion at the gathering, with women, youth and STD-control measures of particular interest to the Mongolian delegates.
For the Mongolians, the Congress is an opportunity to learn from other countries’ successes and failures in the fight against AIDS.
Mongolia’s nine-member delegation includes four doctors – Dr K. Davaajav, head of the AIDS/STD Department of the Research Centre for Infectious Diseases, Health Ministry representative Dr S. Enkhbat. Medical University director Dr Lkhagvasuren and Dr Darisuren from the United Nations Population Fund.
Also in the team are Democrat MPs B. Delgermaa and Saikhanbileg, UNICEF’s B. Bayarmaa and two representatives from women’s NGOs: S. Tsengelmaa from the Women’s Information and Research Centre and N. Chinchuluun, executive director of the Mongolian Women Lawyers Association.
On Sunday, several presentations focused on the difficulties of getting people to use condoms.
In Fiji, studies found the majority of the population was aware of AIDS and had access to condoms, but still chose not to use them.
Lisa Enriquez, a Filipino woman who is HIV-positive, gave a sobering speech on the epidemic.
“One of the most important things I’ve learned from the epidemic is human nature. AIDS is such a humanizing disease. It reminds us of being human, complete with all the weaknesses and imperfections of being human.
“Let us not kid ourselves: changing behaviour is not easy. One doesn’t change because somebody tells him or her to do so.
“We will need to get our act together, institutionalize our efforts and continue working harder with passion and perserverance.”
The Congress continues until October 30.
More on the Congress here: Fourth International Congress on AIDS in Asia and the Pacific
“The Fourth International Congress on AIDS and Asia in the Pacific convened 3,000 scientists, people working in the communities, and people living with HIV/AIDS to discuss the state of AIDS in Asia and the Pacific and how the problem is being addressed now and into the future. The following topics addressed at the Congress are explored: the extent of the HIV epidemic, HIV risk behaviors, women and HIV, clinical manifestations of HIV infection, antiretroviral therapy, and perinatal HIV transmission. HIV is spread differently among these countries and a nation’s wealth largely determines its ability to execute prevention programs and patient access to therapy. Most patients in Asia pay for their own medications. It is hoped that more prosperous and technologically advanced nations will demonstrate stronger leadership and commitment in the fight against AIDS in the region.” Phanuphak P. Fourth International Congress on AIDS in Asia and the Pacific. J Int Assoc Physicians AIDS Care. 1998 Feb;4(2):22-5. PMID: 11365085.
More on HIV/AIDS:
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2020/12/17/lamas-against-aids/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2017/08/15/mongolian-aids-bulletin/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/31/rainforest-rubbers-save-lives/


This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023











You must be logged in to post a comment.