By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

Revolutions in technology are placing more and more power into the hands of the individual, and 3D printing and fabrication machines are opening a whole new chapter.
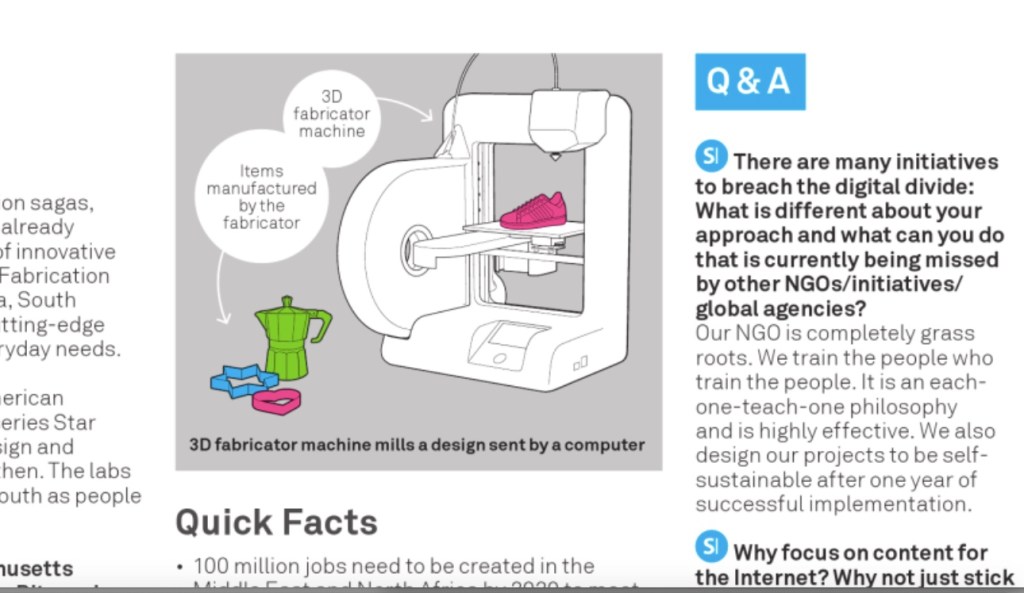
These devices come in many forms, but they all do one thing: they can manufacture pretty well any three-dimensional object on the spot, from digital plans. These machines come in many sizes, from factory scale to smaller, home versions which are no bigger than personal computer printers, such as the well-known MakerBot Replicator 2 (makerbot.com).
3D printers introduce sophisticated precision manufacturing to the individual much in the same way the personal computer and the Internet have empowered people to make their own software, build websites and start online businesses.
A pioneering educational innovation in Chile is taking the technology even further, in a way that is truly mind-blowing. Thinker Thing (thinkerthing.com) promises to transform the way people interact with this new technology. “We have built a machine that will allow you to make real objects with your mind,” its website states.
And, it wants to do more: “We want to use our invention to light a fire of inspiration throughout the remote and often disadvantaged schools of South America and we can do this with your help.”
Thinker Thing allows the user to wear a headset and communicate through brain waves to the 3D printer. The printer then manufactures a three-dimensional model of the thoughts. These can be squiggly shapes or even, it is hoped, more sophisticated forms.
Thinker Thing’s Chilean Chief Technology Officer is George Laskowsky. Laskowsky has a games console engineering background and was a research assistant in charge of high-energy particle experiments.
The Chilean government is funding this experiment to help children to improve their creative skills. The idea is to use the technology to eliminate the technical side of creating objects and focus the effort on the creative thought process. Thinker Thing was selected from more than 1,400 applicants to participate in the prestigious global accelerator program, “Start Up Chile” (http://startupchile.org). Start-Up Chile is a program created by the Chilean government that seeks to attract early-stage high potential entrepreneurs to develop startups using Chile as a platform to go global, in line with the national goal of converting Chile into the innovation and entrepreneurship hub of Latin America.
Based in Santiago, Chile, Laskowsky is seeking support for further development on IndieGoGo (http://www.indiegogo.com/projects/children-creating-real-objects-with-their-mind), an international crowdfunding platform for projects.
The plan is to tour Thinker Thing all around Chile and use the science, art and engineering principles behind the invention to help very young children in remote rural regions to learn through understanding the project. Its creators also hope to take the exhibition – called the Monster Dreamer School Outreach Program and the Fantastical Mind Creatures of Chile Exhibition – on the road and show it in major global cities.
The children are being asked to imagine fantastical creatures that will then be made into 3D forms with the machine. The idea is to then sell these 3D creatures to supporters of the project to help fund the initiative. As well, these creatures will go on display in an exhibition to help educate visitors about Chile’s children and their communities.
To increase interest, exclusive photographic prints and limited edition figurines are available of the creatures the children create.
The prototype uses what is called an EmotivEPOC, basically a wireless neuroheadset collecting signals from the user’s brain. In operation, the software allows users to make 3D models with the power of thought which are then made into a plastic model using a MakerBot Industries Replicator.
This is experimental stuff and neurotechnology is in its early stages. It can detect simple emotions such as excitement or boredom and cognitive thoughts such as push and pull. Despite being in its early stages, the technology can evolve a 3D object over a number of steps by detecting the user’s emotional response to design changes.
Thinker Thing has been working alongside neuroscientists to understand the workings of the brain. Amazingly, in one experiment they were able to get a person to control the leg of a cockroach using their own thoughts. Called the Salt Shaker (http://www.thinkerthing.com/about-2/salt-shaker/), it is an experimental kit for young students and hobbyists that allows them to take control of a biological limb quickly and simply.
The 3D printing revolution is energizing for large and small-scale manufacturers alike. It means a business can now engage in precision manufacturing of products and spare parts quickly. It means it is possible to download from the Internet plans for new innovations and manufacture them within minutes. It also means communities off the mainstream supply line can make what they need and repair machinery without needing to wait weeks or months for items to be shipped from afar or spend vast sums on shipping costs.
The Fab Labs project based at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has been at the forefront of pioneering and prototyping this technology, including running testing labs across the global South to prove the relevance of the technology to the world’s poorest communities.
As of 2012, these include Fab Lab Afghanistan (http://www.fablab.af/), in Chile the FabLab Santiago (www.designlab.uai/fablab), Fab Lab Egypt (www.fablab-egypt.com), in Colombia the FabLab Medellin (http://www.fablabcolombia.com), in Ghana the Takoradi Technical Institute (http://ttifab.wikispaces.com/How+to+Use+the+TTI+Fab+Lab+Wiki), in India at various locations, Indonesia’s HONFablab (http://honfablab.org), ARO FabLab Kenya West (http://www.fablab.co.ke), and in Peru, South Africa, Suriname and many more are in the works (http://fab.cba.mit.edu/about/labs/).
If Thinker Thing has its way, maybe people in the future will say “I think, therefore I print!”
Published: August 2013
Resources
1) Stratasys: The company manufactures 3D printers and materials that create prototypes and manufactured goods directly from 3D CAD files or other 3D content. Stratasys systems are used by manufacturers to create models and prototypes to aid in the new product design process. And they are becoming widely used for production of finished goods in low-volume manufacturing. Systems range from affordable desktop 3D printers to large production systems for direct digital manufacturing. Website: http://www.stratasys.com/
2) 3D Systems: 3D Systems is a leading provider of 3D content-to-print solutions including 3D printers, print materials and on-demand custom parts services for professionals and consumers alike. Website: http://www.3dsystems.com/
ExOne: With decades of manufacturing experience and significant investment in research and product development, ExOne has pioneered the evolution of nontraditional manufacturing. This investment has yielded a new generation of rapid production technology in the field of additive manufacturing as well as advanced micromachining processes. Website: http://www.exone.com/
FabCentral: This site supports a digital fabrication facility and global network of field fab labs managed by MIT’s Center for Bits and Atoms. Website: http://fab.cba.mit.edu
Maker Shed: 3D Printing and Fabrication: An outstanding resource for getting all you need to understand 3D printing and manufacturing, with 3D printers, supplies, Whether you want to print out physical objects or machine something from plastic, wood, or other materials, we have the tools and accessories you need. Website: http://www.makershed.com/3D_Printing_Fabrication_s/220.htm
EMachineShop: The first and leading machine shop designed from the start for the Internet, eMachineShop’s mission is to provide easy, convenient and low-cost fabrication of custom parts via the web. Website: emachineshop.com/
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.
Follow @SouthSouth1
Google Books: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=YfRcAwAAQBAJ&dq=development+challenges+august+2013&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/DavidSouth1/development-challenges-august-2013-issue
Southern Innovator Issue 1: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Q1O54YSE2BgC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 2: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ty0N969dcssC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 3: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=AQNt4YmhZagC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 4: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=9T_n2tA7l4EC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 5: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=6ILdAgAAQBAJ&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023











You must be logged in to post a comment.