By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

Africa’s growth in the past decade has held steady despite the trauma of the global economic crisis and the tumult of the “Arab Spring” in several countries of North Africa. African economies are growing because of a number of resilient trends. These include growing regional trade links, greater investment in infrastructure and the remarkable rise of China to become Africa’s number one trade partner, pushing the United States to second place (Technology + Policy). This has given birth to a growing consumer marketplace and consumer class – some 300 million people earning about US $200 a month (Africa Rising).
The continent as a whole now stands as the 10th largest economy in the world.
How will Africans spend this new money in their pockets (or more than likely, on their mobile phones)? They could go for the big, famous global brands that they see advertised in magazines or on television. Or they could also spend it on local products and services that seem just as enticing and life-improving. Creating local African products and services with strong brands will have an important knock-on effect of creating new wealth and jobs within Africa.
One new product being introduced to the West African country of Ghana’s thirsty beer drinkers is the Eagle beer brand. But this is not just any beer made from the traditional ingredients of water, hops, malted barley and yeast (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beer) – it is brewed from the root vegetable cassava.
A staple of many African diets, cassava (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cassava) is a starchy, tuberous root vegetable and a common crop across the continent.
It is believed that 70 per cent of Ghana’s farms are just 3 hectares in size or smaller. They grow many things, but cassava is the most common crop.
Cassava soon spoils once it has been harvested and needs to be consumed quickly. Currently, too much of it goes to waste. In Ghana, according to The Guardian, there is an annual surplus of some 40 per cent of cassava produced.
The Accra Brewery Limited (ABL) (http://www.sabmiller.com/index.asp?pageid=1156) decided to find a way to put the cassava from smallholder farms to good use and stop the waste. The brewery had observed the success of parent company SABMiller (http://www.sabmiller.com/index.asp?pageid=27) elsewhere in Africa, in turning cassava and the grain sorghum from smallholder farmers into beer. Farmers had directly benefited from the purchase of their surplus product.
Eagle brand cassava beer is creating opportunities for business, consumers and smallholder farmers in Ghana. According to The Guardian, the company hopes to source cassava from 1,500 smallholders.
By having a guaranteed purchase from the brewery on a regular basis, farmers are able to move beyond subsistence agriculture and turn themselves into functioning businesses.
The spare income from selling the cassava also can be used to improve a farmer’s household access to healthcare and education.
The Accra Brewery provides advice on agricultural techniques and growing a diverse range of crops, to ensure farmers are not dependent on a monocrop harvest. It also offers advice on business and developing commercial relationships.
The Eagle brand cassava beer will be sold at a 30 per cent discount to low-income drinkers in order to lure them away from illicit and informal alcohol drinks of dubious quality.
Professor Ethan Kapstein of business school INSEAD found that ABL and its water business Voltic (GH) Ltd. was a creator and supporter of high-quality jobs in Ghana and supported 17,600 jobs throughout the Ghanaian economy.
Adjoba Kyiamah (http://www.sabmiller.com/index.asp?pageid=1766&blogid=172), corporate and legal affairs director at Accra Brewery, told The Guardian she believes Eagle brand beer will help create even more jobs, boost government revenues and expand consumer choice.
This is an innovative first, as cassava beer had never been made before in Ghana on a commercial scale. This had not been possible in the past because of the challenge of collecting fresh cassava from farms widely spread out over a large territory. As well as spoiling quickly, Cassava is heavy, being mostly made up of water, and is difficult to transport over large distances.
“Part of our strategy across Africa is to make high quality beer which is affordable for low-income consumers while simultaneously creating opportunities for smallholder farmers in our markets. The launch of Eagle in Ghana ticks both these boxes,” said Mark Bowman, Managing Director of SABMiller Africa.
“Eagle is aimed at attracting low-income consumers away from illicit alcohol. This is a virtuous circle: smallholder cassava farmers have a guaranteed market for their crop, which is then used to make consistently high quality, affordable beer for consumers; and the government realises increased revenues as people trade up into formal, taxable alcohol consumption.”
ABL is using a mobile processing unit developed by DADTCO (Dutch Agricultural Development and Trading Company) Cassava Processing Ghana Ltd. It is designed to process the cassava on site, preserving the integrity of the starch.
Eagle is sold in 375 millilitre bottles at a price 70 per cent lower than that charged for other lager beers. The use of local ingredients, and a reduced excise tax awarded to the brand because is it is boosting local agriculture, allows for the lower price.
Production of cassava beer got its start first in Mozambique, with the launch of the Impala brand (http://www.sabmiller.com/index.asp?pageid=149&newsid=1748), the first commercial-scale cassava-based clear beer, in October 2011.
Published: April 2013
Resources
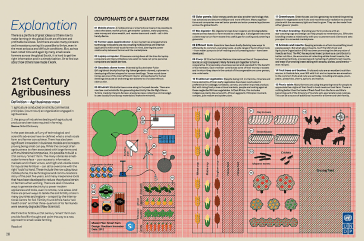
1) Southern Innovator Magazine Issue 3: Agribusiness and Food Security. Packed with information, insights and business models to turn smallholder farmers into agribusinesses. Website: http://www.scribd.com/doc/106055665/Southern-Innovator-Magazine-Issue-3-Agribusiness-and-Food-Security
2) Cassava can become Africa’s new cash crop: Cassava is abundant in sub-Saharan Africa, and could be an ideal crop to improve food security for millions of people. Website: http://www.guardian.co.uk/global-development-professionals-network/2013/mar/28/cassava-food-security-sub-saharan-africa
3) Cassava recipes from the BBC. Website: http://www.bbc.co.uk/food/cassava

London Edit
31 July 2013

Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.


This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2022












You must be logged in to post a comment.