By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

Agriculture around the world produces a great deal of waste as a by-product. It can be animal faeces, or the discarded plant husks thrown away when rice, grains or maize are harvested. When this waste meets the urgent need for electricity, something special can happen.
The number of people still without electricity in the South is vast. The failure of major electricity generating power stations to reach so many people has spurred entrepreneurs to come to the rescue. Power is critical to so many things: small businesses need it, anyone wanting access to computers and the Internet needs it, and modern appliances like refrigerators run on it. During the past 25 years, electricity supplies have been extended to 1.3 billion people living in developing countries. Yet despite these advances, roughly 1.6 billion people, a quarter of the global population, still have no access to electricity and some 2.4 billion people rely on traditional biomass fuels, including wood, agricultural residues and dung, for cooking and heating. More than 99 percent of people without electricity live in developing regions, and four out of five live in rural areas of South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa (International Energy Agency, IEA).
Power outages in Africa are a serious and frequent problem and a significant force holding back development. With global oil prices on the rise, turning to diesel generators is an expensive option.
According to the IEA, the lack of electricity leaves poor countries “trapped in a vicious circle of poverty, social instability and underdevelopment.”
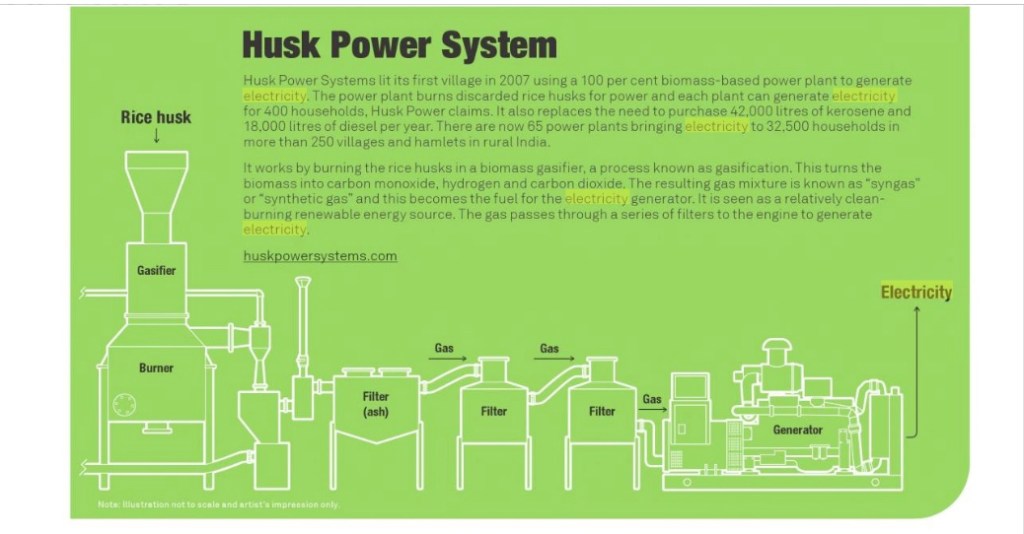
In India, 80,000 of the country’s half a million villages lack electricity. Two students, Charles Ransler and Manoj Sinha, have started a business providing electricity to some of these villages by turning rice husks – a by-product of rice milling – into gas that then powers an electricity generator.
Already, two of their rice-burning generators are providing electricity to 10,000 rural Indians. The hope is to rapidly expand the business to hundreds of small village power plants.
The business, Husk Power Systems, was started while the two were at the University of Virginia’s Darden School of Business.
While the generator burns the rice husks to make a gas to produce electricity, it also leaves behind a waste product of ash that is sold as an ingredient in cement.
This technology can provide off-grid power to rural Indian villages of 200 to 500 households. Using the husk-powered mini power plant, the team plans to offset close to 200 tons of carbon emissions per village, per year in India.
The idea for the rice husk generators was originally conceived by Sinha and Gyanesh Pandey, the third partner in Husk Power, who left an engineering career in Los Angeles to return to India and oversee the rice husk project. Sinha and Pandey went to college together in India and both come from rural Indian villages that struggle with a lack of electricity.
“We grew up in those areas,” said Sinha. “Our relatives still do not have electricity. We wanted to give back to those areas.” Originally they envisioned refining the generator concept and raising enough money to donate rice-husk generators for two or three villages near where they grew up, said Sinha.
But instead, after some research, they realised it could be a financially viable business expandable to hundreds of villages. There are 480 million Indians with no power and 350 million of them live in rural villages, concentrated in eastern India’s “Rice Belt,” where the villagers are “rice rich and power poor,” said Ransler.
The project has already won a fistful of prizes, including US$50,000 from the Social Innovation Competition at the University of Texas.
They think that each rice husk generator is to break even in about two and a half years.
And they like to think this is the Starbucks of off-grid electricity generation, potentially as successful as the globe-spanning US coffee shop chain. “You can put one of these in 125,000 locations, hire local people, and turn a raw material into money – just substitute rice husks for coffee beans,” said Ransler.
Another maker of biomass mini power plants in India is Decentralised Energy Systems India (DESI power). It is a New Delhi-based non-profit company specialising in building a decentralised power network for rural India. It was formed by Development Alternatives, India’s largest sustainable development NGO. It is able to provide a megawatt of electricity to a village for the cost of 44 million rupees, rather than 57 million rupees from the central grid.
Published: June 2008
Resources
- Global Social Venture Competition.
Website: http://www.haas.berkeley.edu/responsiblebusiness/GSVC2008CallforEntrants.html - Ignite Clean Energy Competition sponsored by MIT.
Website: http://www.ignitecleanenergy.com/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/06/battery-business-brings-tanzanians-cheap-electricity/

Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.



https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/03/05/southern-innovator-issue-5/

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2022














You must be logged in to post a comment.