By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

By 2030, some 5 billion people around the world will live in cities. Next year, 2008, is predicted to be the tipping point, when urban dwellers (3.3 billion people) will outnumber rural residents for the first time. These are the conclusions of UNFPA’s State of the World Population 2007 Report. Even more strikingly, the cities of Africa and Asia are growing by a million people a week. And 72 percent of the population in sub-Saharan Africa live in slum conditions.
But as populations grow — and most will be poor, unemployed and under 25 — it becomes critical that effective solutions are found to ensure people can live with dignity and comfort. And design is being used more and more to overcome this challenge.
George Martine, author of the UNFPA report, is blunt: “We’re at a crossroads and can still make decisions which will make cities sustainable. If we don’t make the right decisions the result will be chaos,” he told the UK newspaper The Independent.
Guatemala-born architect Teddy Cruz of Estudio Teddy Cruz in San Diego, California, joins a small but growing number of socially responsible architects. He applies a concept more associated with middle class shoppers at the furniture design emporium Ikea to the world’s estimated one billion urban slum dwellers (UN-Habitat). Without legal title to the land they live on, packed tightly into densely overcrowded shantytowns, most squatters and slum dwellers live in makeshift homes made from whatever they can get their hands on. This is estimated to include half the urban population of Africa, a third of Asia and a fourth of Latin America and the Caribbean (Click here for more information).
The ad-hoc shelters and houses they build can be dangerously unstable, and vulnerable to natural disaster from flash floods to earthquakes. Cruz had noticed that while building supplies and materials were plentiful, nobody was selling safe and affordable housing frames for slum dwellers. According to the International Labor Organization, formal housing markets in developing countries rarely supply more than 20 percent of housing stock.
Cruz’s solution was to design a simple kit for building the frames for a house or a business that he now sells in Mexico. Each customer receives a manual, a snap-in water tank, and 36 frames that can be assembled in many configurations, or serve as a frame for poured concrete. These sturdy frames can also be added to with locally found materials. Cruz said he was inspired by “the resourcefulness of poverty” and by the cheap and affordable pre-fabricated homes that once were sold by catalogue by the American retailer Sears.
Cruz has been testing the structures in Tijuana, Mexico – a rapidly growing city on the border with the United States and a destination for Mexico’s poor. His work as an architect has centred on exploring how informal settlements grow faster than the cities they surround. These settlements, he says, break the rules and blur the boundaries between what is urban, suburban and rural. Cruz’s frame kits can be used to build a home, or combination of home and business, acknowledging the fact many people need to use their home as a business for a livelihood.
“These start-up communities gradually evolve,” said Cruz., ”or violently explode out of conditions of social emergency, and are defined by the negotiation of territorial boundaries, the ingenious recycling of materials, and human resourcefulness.”
Published: July 2007
Resources
- More Urban, Less Poor: The first textbook to explore urban development and management and challenge the notion unplanned shanty towns without basic services are the inevitable consequence of urbanization.
- Slum Populations in the Developing World: A map showing the African countries with large slum populations and their percentage of the total population
- A UN regional project to tackle the issue of housing the urban poor
- Architecture for Humanity: An NGO to promote architectural and design solutions to global, social and humanitarian crises.
There are many ways to play around with your dwelling and architecture ideas. Here are some products available online:
- Arckit: Arckit is a tangible and hands-on design tool for spontaneously bringing your architectural ideas to life right before your eyes. Website: https://www.arckit.com
- SmartLab Archi-TECH Electronic Smart House: Build your house and power it up! This creative STEAM toy allows aspiring architects and engineers to design and build modular structures – and then power them up with lights, sounds, sensors, and motorized parts! Website: https://www.mastermindtoys.com/products/smart-lab-archi-tech-electronic-smart-house
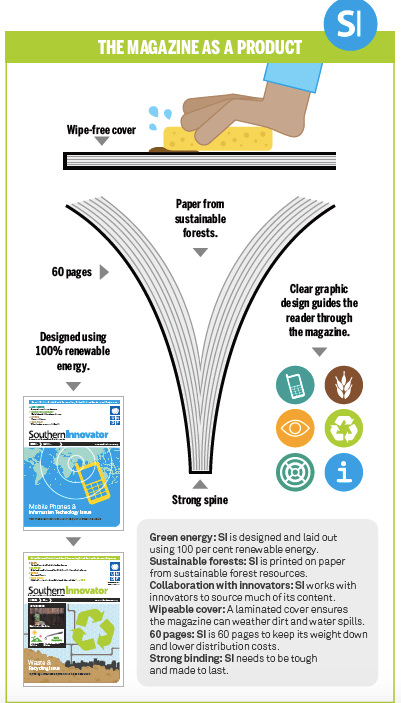
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.
Follow @SouthSouth1
Like this story? Here is a dirty secret: this website is packed with stories about global South innovators. We spent 7 years researching and documenting these stories around the world. We interviewed the innovators to learn from them and we visited them to see how they did it. Why not use the Search bar at the top and tap in a topic and see what stories come up? So, stick around and read some more!
Archive.org: https://archive.org/details/Httpwww.slideshare.netDavidSouth1development-challengessouthsouthsolutionsjuly2007issue
Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/DavidSouth1/development-challengessouthsouthsolutionsjuly2007issue
Southern Innovator Issue 1: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Q1O54YSE2BgC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 2: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ty0N969dcssC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 3: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=AQNt4YmhZagC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 4: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=9T_n2tA7l4EC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 5: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=6ILdAgAAQBAJ&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023




















You must be logged in to post a comment.