By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

A highly innovative new way to teach the basics of electronics, computing and technological innovation is being pioneered in the slums of Nairobi, Kenya. Driven by the desire to counter perceptions of apathy among young people, NGO Kuweni Serious is running a training course for girls aged over 8 years in some of the poorest parts of the city to turn on a new generation to the power of technology to make change.
“Technology is pivotal in our work, as Kuweni Serious is a primarily online platform that seeks to create offline action,” according to Kuweni Serious’ Rachel Gichengo. “It’s positive in that you can reach a lot of people with solid messages that are in bite-size pieces that are easy to disseminate and consume. Everyone can pass on the information with a simple click – it’s an easier way to begin socio-political discussion among people who would otherwise not be drawn into these kinds of discussions because they’re not presented in a way that appeals to them. The typical profile of a KS volunteer is someone in their 20s, middle-class, has some experience volunteering, has never been to a slum despite living in Nairobi, but wants more for their country.”
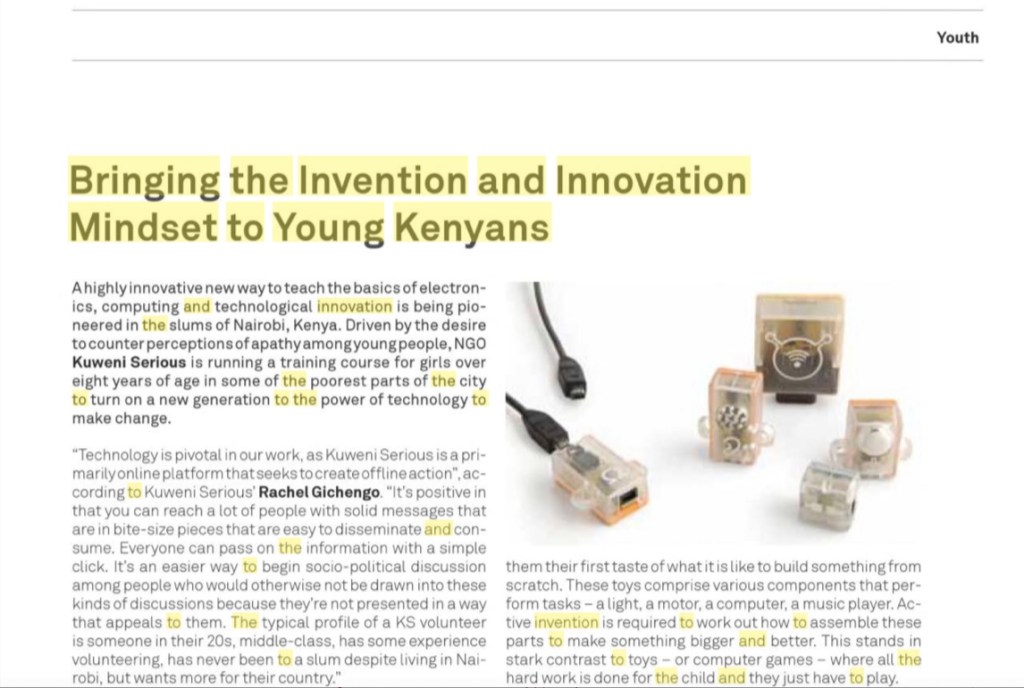
The course uses a clever, hands-on approach to teaching. Instructors use a new generation of learning toys that help young people understand how technology works and gives them the first taste of what it is like to build something from scratch. These toys comprise various components that perform tasks – a light, a motor, a computer, a music player. Active invention is required to work out how to assemble these parts to make something bigger and better. This stands in stark contrast to toys – or computer games – where all the hard work is done for the child and they just have to play.
“We chose tech training because it’s a traditionally under-represented area when it comes to reaching this particular group (underprivileged girls), yet such an important set of skills to be taught in this day and age,” confirms Gichengo. “We want to expand these girls’ thinking – to get them interested in the possibilities of careers in science and tech, rather than perpetuate the idea that all they’ll ever do, based on their circumstances, is tailoring or dance. We hoped to open our girls’ worlds a bit, as well as link them to our Kuweni Serious community of volunteers.”
Called PicoCrickets (www.picocricket.com), and manufactured by the Canadian Playful Invention Company (PICO), the toys were developed from research and ideas at the Lifelong Kindergarten group (http://llk.media.mit.edu/) at the MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) Media Lab (www.media.mit.edu).
“Pico Crickets are cool,” continues Gichengo. “They’re a fun way to learn to build things, to learn the connection between hardware and software, to begin to understand what computers can do. They make learning easy, and they make science seem accessible to a group that tends to see it as too hard for them. The kits were paid for by a grant from the Girl Effect (www.girleffect.org).”
The MIT lab conducted intensive research into creative learning environments for children. One of the first fruits of this research was Lego Mindstorms (http://mindstorms.lego.com), kits that allow children to make and program their own robots.
Inspired by this work, the PicoCricket places more emphasises on artistic expression. The company created the PicoCricket Kit (www.picocricket.com/whatisit.html) as a way to integrate art and technology to “spark creative thinking in girls and boys 8 years and older,” according to its website.
A typical kit includes a central PicoCricket that a child then plugs in to various motors, sensors, lights and other devices to make something that can spin, light up or play music. It is intended to give free rein to both technological innovation and artistic expression.
Kenya experienced violent rioting during the 2007 and 2008 elections. The shock of the events produced a number of initiatives to counter the violence and the social and economic disruption it has caused. One of the most well-known innovations, Ushahidi (www.ushahidi.com), a crisis-mapping platform, has been deployed around the world and led to many other new innovations.
Kuweni Serious (www.kuweniserious.org) is also a result of this crisis. The NGO sets out to counter the stereotype of Kenya’s youth as a “hedonistic generation of brand-obsessed youth, moving from party to party in the night and congregating on Facebook during the day.”
Kuweni Serious believes young people in Kenya were shocked into action when violence broke out during the elections. Prices jumped for everything – from fuel to food – and water and power started to be rationed. It was a wake-up call to youth: it was getting harder and harder to ignore what was happening in the country.
Kuweni Serious was founded by Kenyan youth and asked the question “how do Kenya’s youth feel about all the chaos around us?” It seeks to rally young people to their motto: “Fighting the evil forces of apathy.”
Their 125/100 program set out to train 125 girls on a 100-day course. It ended with a graduation ceremony on July 2, 2011.
The program, run by volunteers from the University of Nairobi, has taught basic computer skills, got the children working on Google Maps and making – and inventing – using the PicoCrickets.
The girls on the course came from Baba Dogo and Kibera, Nairobi’s largest slum.
The technology training program lasted between three and six hours a week for 12 weeks. The inventions made by the children included merry go rounds, a lamp stand and fan and miniature automobiles. Participants even got to grips with Google Maps and learned how to use mobile phones in citizen journalism. At the end of the course, all the children received a certificate reinforcing their sense of accomplishment and achievement.
“We hope to continue doing similar projects, scaling up 125/100, and working on developing a corps of everyday change makers among young, educated, middle class Kenyans,” according to Gichengo. “We’re also preparing for the 2012 elections, so we need to have more conversations about what a new election means, given the outcome of our previous one.”
Another initiative seeking to improve life chances for Kenyan girls is ZanaAfrica (www.zanaa.org). It focuses on educational opportunities for girls, consulting them to find out what would increase their chances of graduation from school. Because of this back-and-forth dialogue with the girls, they have come up with various strategic programs, one example being providing girls with sanitary pads for menstruation (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Menstruation) every month so that they do not skip classes and lose vital class time. ZanaAfrica was born around tackling the issue of lost school days for girls because of poor provision of sanitary pads in Kenya: an estimated 868,000 adolescent girls were missing 3.5 million school days a month, according to ZanaAfrica. Sanitary pads in Kenya cost twice most people’s daily wage. Just to provide pads to all the school girls in Kenya, they estimated, would cost US $13 million a year, increasing by 5 percent every year.
Another disadvantage for these girls is finding the right support environment and strong, positive role models. ZanaAfrica’s solution is Empowerment Clubs (www.zanaa.org/empowernet-clubs), places where small groups of 15 to 20 students meet with field officers and tackle difficult topics not discussed at home or in school: drugs, relationships, self-confidence, health and disease. There are already 1,000 students in the Kibera area in these Empowerment Clubs. This approach has also been combined with something called EmpowerNet Clubs: these clubs take place in the schools and combine blogging and tweeting (www.twitter.com) with the discussions on life issues. Already in five schools, the clubs include a field officer and 20 girls meeting once a week.
ZanaAfrica was started in 2007 by social entrepreneur and Harvard University graduate Megan White, who has been living and working in Kenya since 2001. ZanaAfrica identifies poverty-eradicating, African-led innovations and then tries to build them up and find ways to replicate them and make them sustainable. They look for innovations in the areas of health, education and the environment.
“Kenyans are definitely early adopters, and are rushing to take advantage of new technologies,” confirms Gichengo. “The Kenyan success stories have been a huge inspiration, largely because they developed localized solutions that could then be exported to the world, rather than the other way around, which tends to be the case. There’s always value in looking further afield to see what else is being done around the world, but the iHub and Ushahidi (and the Kenya ICT Board, Safaricom, etc.) have gone a long, long way in inspiring local innovation.”
Published: July 2011
Resources
1) Make Magazine: “MAKE Magazine brings the do-it-yourself mindset to all the technology in your life. MAKE is loaded with exciting projects that help you make the most of your technology at home and away from home. We celebrate your right to tweak, hack, and bend any technology to your own will.” Website: http://makezine.com/
2) Lego Mindstorms robot-making kits. Website:http://mindstorms.lego.com/en-us/Default.aspx
3) Southern Innovator Issue 1: New global magazine celebrating innovation across the global South. Website:http://www.scribd.com/doc/57980406/Southern-Innovator-Issue-1
4) iHub Nairobi: iHub Nairobi’s Innovation Hub for the technology community is an open space for the technologists, investors, tech companies and hackers in the area. This space is a tech community facility with a focus on young entrepreneurs, web and mobile phone programmers, designers and researchers. It is part open community workspace (co-working), part vector for investors and VCs and part incubator. Website:http://ihub.co.ke/pages/home.php
5) Maker Faire Africa 2011: MFA 2011 continues to cultivate new and existing maker communities across Africa. As was the case in Accra (‘09) and Nairobi (’10), MFA 2011 will present and spotlight the vibrant and endlessly creative individuals that have come to represent the spirit of ‘making’ throughout the continent. These innovators, artists and tinkerers will be exhibiting a fusion of the informal and formal; ideas, inventions, hacks and designs both low-tech & high-tech. From cuisine to machines, come see their re-imagining of products, exploration of novel materials, and original solutions for some of the continent’s most important challenges and opportunities. Maker Faire Africa 2011 will be a celebratory showcase of unhindered experimentation and curiosity. Website:http://makerfaireafrica.com/2011/06/09/maker-faire-africa-2011-cairo/
6) Social enterprise (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Social_enterprise): Learn more about the vibrant world of social enterprise and connect with others. Website: http://www.socialenterpriselive.com/

Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.




This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023









You must be logged in to post a comment.