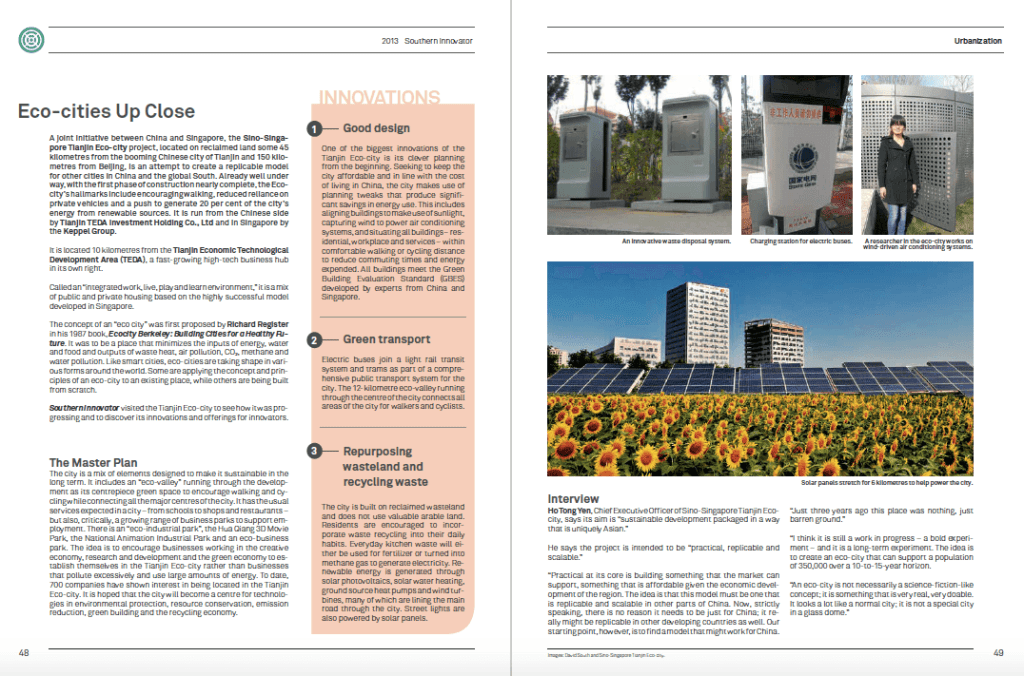
By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

There is a pressing need to spread access to the internet to the world’s poor — but also many obstacles. Often it is something as basic as a lack of electricity that brings progress to a halt. But a Brazilian innovator has come up with a solar power supply that is helping to bring internet access to schools serving the poor.
Many initiatives are trying to bring inexpensive access to the internet to rural and remote regions around the world. Schools in poor areas are receiving laptop computers through schemes like the One Laptop Per Child project, but it is common that schools do not have a steady electricity supply to power the computers or the internet connection. One of the most successful ways of rapidly expanding access is to offer wireless (WiFi) internet so that anyone can use the Web, no matter what device they have, whether a laptop computer, a personal computer or a mobile phone. The signals use radio waves, and are an excellent solution for multiple users.
Brazilian professor Marcelo Zuffo, Interactive Electronics Coordinator at the University of Sao Paulo, has invented a cheap solar-powered WiFi access point for the poor. Designed to be used by schools without a steady source of electricity, it doesn’t need outside electricity supply, and is not difficult to assemble. It is being tested on lampposts around the Sao Paolo campus.
The device uses something called a ‘mesh’ strategy. By acting as a group, several units are able to expand the area covered by WiFi in a honeycomb pattern. The signal is relayed back and forth between the units, significantly increasing the area covered that can access the Web. “In such a strategy,” said Zuffo,”you can cover large rural areas, parks, low income neighbourhoods, by just dropping our equipment in roofs, trees or on to existing lamp posts.”
Zuffo was inspired to develop the solar-powered WiFi boxes after the university tried to bring laptop computers to a Sao Paulo school, and found they didn’t have a steady electricity supply.
“We came up with the idea of taking energy that is most plentiful and cheap, i.e. the sun,” he told the BBC. “We have a solar panel, a cheap motorcycle battery and a circuit that is responsible for energy management. We can have up to two days of full internet coverage and our goal is to increase that to 10 days – so that in the rainy season and the winter, you can have the internet for free.
“The natural plan is to miniaturize the system so that we can save on costs. So by the end you can imagine these WiFi solar mesh devices being the size of a cellphone or playing card.”
The low cost, solar-powered access point is ready as soon as it is unpacked and needs neither maintenance nor a power socket to get going.
“It is a completely autonomous WiFi hotspot, it doesn’t need any internet or energy connection,” said Zuffo.
“Everything comes from the sun and we have plenty of that in Brazil,” he said.
The volunteer organization Green WiFi initiative is also developing solar powered technologies to bring ubiquitous internet access to the world’s poor.
Zufo’s message for other scientists and inventors is this: “Innovation, invention is all about transforming people’s lives. We need methods and equipment which are cheap enough so that they are accessible to virtually every one, suitable for small scale applications, and compatible with man’s need for creativity.”
The issue of inequality in access to the internet has stark consequences for global economic development. Already, according to the World Information Society Report 2007, “Europe has achieved the largest overall gain in digital opportunity over the last two years, followed by the Americas… Asia and Africa have witnessed smaller gains in digital opportunity. The implications for the digital divide are clear: digital opportunity is becoming more sharply divided by region, not less.”
Published: November 2008
Resources
- Wireless Networking in the Developing World: A Practical Guide to Planning and Building Low-cost Telecommunications Infrastructure. Website:
- World Information Society Report 2007: A progress report on pledges to bring digital opportunity to all. Website:
- The Wireless Geographic Logging Engine: This is a website with maps tracking the presence of WiFi access around the globe. So far it maps over 10 million separate WiFi networks. Entrepreneurs only have to log into the website to start searching for wireless networks near them.
- iTrike: The world’s first solar powered wireless internet rickshaw.
- The KyaTera lab where the technology was developed. Website: http://kyatera.incubadora.fapesp.br/portal/research/laboratories/interactive-electronic-media

Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.








This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023











You must be logged in to post a comment.