By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

The world’s population is becoming more urban by the day. By 2030, some five billion people around the world will live in cities. This year is the tipping point: urban dwellers (3.3 billion people) now outnumber rural residents for the first time (UNFPA’s State of the World Population 2007 Report).
But with rising food prices across the globe, many city-dwellers are experiencing hunger and real hardship. On international commodity markets, food prices have gone up 54 percent over the last year, with cereal prices soaring 92 percent (FAO – World Food Situation). While living in an urban environment means living cheek-by-jowl with other people, it doesn’t mean there aren’t ways to grow food and supplement urban dwellers’ tight budgets and boost diets.
U.N. Secretary General Ban Ki-moon has called for food production to increase 50 percent by 2030 just to meet rising demand – and right now there are 862 million people undernourished (FAO). But one solution, urban farming, can make a huge difference, as the Caribbean island of Cuba has shown.
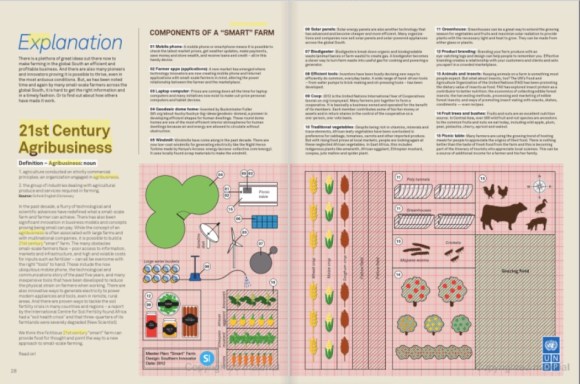
Today, Cuba imports about 50 percent of its minimum fuel and food requirements – a cost that reached US $1.6 billion last year for food. (Reuters). The island has been buffeted by one food crisis after another in the past two decades, first by the collapse of its aid from the Soviet Union, and then by a fuel crisis. But now, urban farming in Cuba provides most of the country’s vegetables, thanks to urban gardens that have sprung up on abandoned land in the country’s cities and towns. And the food is pesticide-free: 70 percent of the vegetables and herbs on the island are organic (http://www.soilassociation.org/web/sa/saweb.nsf/Living/ whatisorganic.html).
These urban farms mean fresh food is just a short walk away from the people who eat it. And in a world of rising fuel prices, Cuba has reduced the use of fossil fuels in the production and transportation of food.
The urban farms have created 350,000 jobs that pay better than most government jobs. It has also improved Cuban’s health: many have moved from diets dominated by rice and beans and imported canned goods from Eastern Europe, to fresh vegetables and fruits.
While Cubans receive at least a basic state ration of rice, beans and cooking oil, the rations do not include fresh fruit and vegetables. After the withdrawal of Soviet subsidies, the average Cuban’s daily calorie intake fell sharply. Between 1989 and 1993, daily calorie intake dropped from 3,004 to 2,323 (UN). But with the growth of urban farms, this has moved up to 3,547 calories a day – even higher than the amount recommended for Americans by the US government.
The secret to this success has been the rise of entrepreneurs like Miladis Bouza, a 48-year-old former research biologist who had to abandon a comfortable middle class life after the collapse of the Soviet Union. Her government salary dropped to US $3 a month. Unable to make ends meet and provide food for her family, she quit her job.
The Cuban government allowed people to turn unused urban land into mini farms. The cities have many vacant lots because the state owns most land and there isn’t competition from private developers, as in many other countries. Unusually for communist Cuba, 80 percent of the profits are kept by the farmers. This can be an average wage of US $71 per month.
“Those salaries are higher than doctors, than lawyers,” Roberto Perez, an agronomist who runs the country’s first urban farm, told The Associated Press. “The more they produce, the more they make. That’s fundamental to get high productivity.”
Miladis grabbed this opportunity to farm a half-acre plot near her home in Havana. Along with her husband, she grows tomatoes, sweet potatoes and spinach, and sells the vegetables at a stall on nearby busy street. This has enabled her monthly income to rise to between US $100 per month and US $250 per month, far more than the average government salary of US $19 per month.
Cuba was inspired by greenbelt farms in Shanghai (http://en.shac.gov.cn/hjgl/jqgk/t20030805_82028.htm): but Cuba has gone even further to make urban farming a key part of the national food supply.
All this urban farming is also all-natural farming. Farms have had to turn to natural compost as fertilizer, and natural pesticides like strong-smelling celery to ward off insects.
So-called organoponicos (http://academicos.cualtos.udg.mx/Pecuarios/ PagWebEP/Lecturas/ORGANOPONICOS.htm ) gather together a wide variety of vegetables, fruits and herbs, as well as ornamental plants. Customers are offered mangos, plantains, basil, parsley, lettuce, garlic, celery, scallions, collard greens, black beans, watermelon, tomatoes, malanga, spinach and sweet potatoes.
“Nobody used to eat vegetables,” said David Leon, 50, buying two pounds of Swiss chard at a Havana organoponico. “People’s nutrition has improved a lot. It’s a lot healthier. And it tastes good.”
Published: June 2008
Resources
- Square Foot Gardening: a book with all the details on how to grow food in tight, urban spaces.
- Urban Gardening Help: a website dedicated to tips for urban gardeners, with resources on urban food production.
Website: http://www.urbangardeninghelp.com/small.htm - Small Urban Gardens: a book covering case studies of urban gardens from around the world.
Website: http://www.amazon.co.uk/Small-Urban-Gardens-Evergreen/dp/3822851418 - An interactive map showing how the world food crisis is affecting countries.
Website: http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/d8184634-07cc-11dd-a922-0000779fd2ac.html?from=text&nclick_check=1
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2020/12/14/african-farming-wisdom-now-scientifically-proven/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/10/cheap-farming-kit-hopes-to-help-more-become-farmers/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2023/01/16/hip-driven-pump-brings-water-to-parched-fields/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/23/kenyan-farmer-uses-internet-to-boost-potato-farm/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/11/09/pocket-friendly-solution-to-help-farmers-go-organic/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/18/woman-wants-african-farming-to-be-cool/

Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.

https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/03/05/southern-innovator-issue-3/

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023








You must be logged in to post a comment.