By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

A couple of enterprising Kenyan engineering students are showing how mobile phones are an inventor’s dream. Their two inventions – one a way to re-charge phones while bicycling, the other an aid for catching fish – show the potential for adapting this technology to the needs of the poor.
The rapid spread of mobile phones across the South is giving rise to a flurry of invention and experimentation. While many of the new mobile phone-users do not have much money, they are often driven by poverty to invent solutions – and in so doing prove the phones offer many ways to generate income.
According to the International Telecommunications Union (ITU), Africa is the world’s fastest-growing mobile phone market, and the number of subscribers surpassed 300 million in 2008. The number of mobile phone users in the world passed 4 billion in 2008, and the fastest growth was in the South (ITU). The trend towards increasing development of inexpensive handsets means more phones will be reaching even more poor people in the future.
Kenya has seen blistering growth in mobile phone ownership: from just 200,000 users in 2000, there are now more than 17.5 million people with mobile phones out of a population of 38.5 million
As powerful as mobile phones are, they need electricity to keep working. The struggle to find a steady supply of electricity vexes many in the South, so finding cheap or free ways to recharge the phones represents a huge market opportunity.
While mobile phone recharging has become a business in its own right across the South, it is costly as well as time-consuming. Some people spend hours just getting to recharging stations.
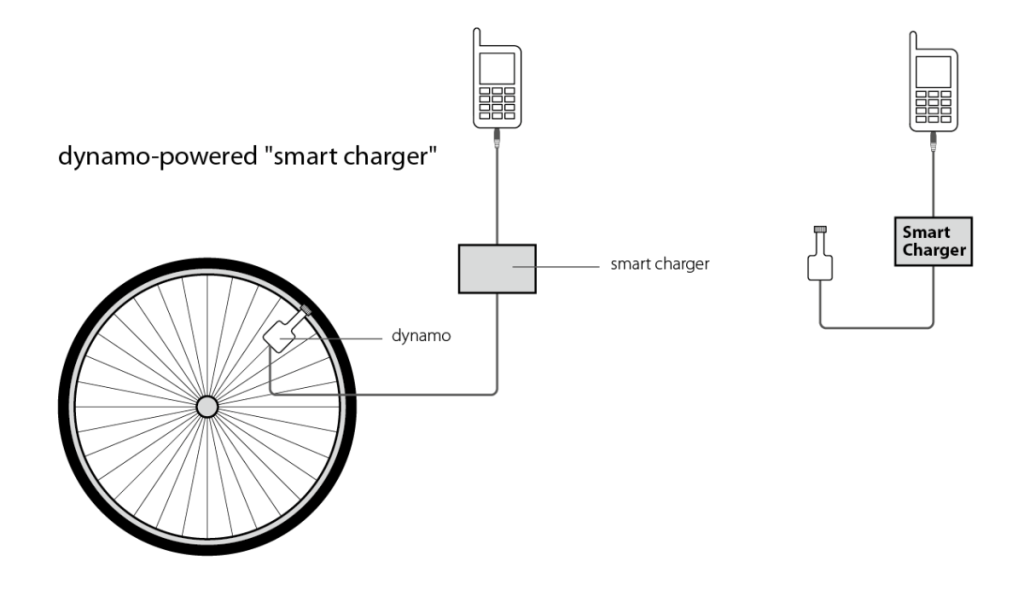
To tackle this chronic problem, Engineering students Pascal Katana and Jeremiah Murimi of the Department of Electrical and Information Engineering at the University of Nairobi, Kenya (http://uonbi.ac.ke/departments/index.php?dept_code=HE&fac_code=32) have invented a device called the “smart charger.” It is powered by the dynamo that is standard issue with most bicycles sold in Kenya. Dynamos on the bicycle’s back wheel are little electricity generators that use pedal power to illuminate the bike’s lights.
It takes an hour to charge the mobile phone by peddling the bicycle: around the same time it takes to charge a phone using an electricity plug. A one-time charge for somebody can cost up to US $2 at a recharging service. But the smart charger sells for 350 Kenyan shillings (US $4.50) – around the cost of two charges.
“We both come from villages and we know the problems,” Murimi told the BBC.
“The device is so small you can put it in your pocket with your phone while you are on your bike.”
The smart charger has been assembled from bits and pieces the duo found: “We took most of (the) items from a junk yard,” Katana said. “Using bits from spoilt radios and spoilt televisions.”
To test the experimental device, workers at the university campus were recruited to have a go.
“I use a bicycle especially when I’m at home in the rural areas, where we travel a lot,” said campus security guard David Nyangoro. “It’s very expensive nowadays charging a phone. With the new charger I hope it will be more economical, as once you have bought it, things will be easier for you and no more expenses.”
Kenya’s National Council for Science and Technology (http://www.ncst.go.ke/) has now backed the project and the students are exploring ways to mass-produce the smart charger.
Another invention by Katana has adapted a mobile phone to improve fishermen’s success, according to Afrigadget (www.afrigadget.com). It amplifies the sounds made by fish as they feed. As the sound is broadcast outwards from the feeding, other fish are attracted to the same place, believing there is more food. A GPRS/GSM (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/General_Packet_Radio_Service) mechanism in the fishing net is triggered when there is enough fish in the net, and an SMS text message is sent to the fisherman letting him know it is time to haul in the net.
It looks like Pascal Katana can re-charge your phone and fill your plate!
Published: August 2009
Resources
1) Entrepreneurs can track the growth of the mobile phones market here. Website: http://www.wirelessintelligence.com
2) SMS Bootcamp: The “SMS Boot Camp” at the University of Nairobi, is a project-based course enabling teams of students to launch and market their own SMS services to the millions of mobile phone users in Kenya. A small amount of seed funding will be available to the best teams interested in turning their project into a commercial venture. Website: http://eprom.mit.edu/entrepreneurship.html
3) Mobile Active.org: MobileActive.org is a community of people and organizations using mobile phones for social impact. They are committed to increasing the effectiveness of NGOs around the world who recognize that the over 4 billion mobile phones provide unprecedented opportunities for organizing, communications, and service and information delivery. Website: www.mobileactive.org
4) Textually.org: is the entry point of three weblogs devoted to cell phones and mobile content, focusing on text messaging and cell phone usage around the world, tracking the latest news and social impact of these new technologies. Website: http://www.textually.org/
5) Ushahidi: is a website that was developed to map reports of violence in Kenya after the post-election fallout at the beginning of 2008. The new Ushahidi Engine is being created to use the lessons learned from Kenya to create a platform that allows anyone around the world to set up their own way to gather reports by mobile phone, email and the web – and map them. It is being built so that it can grow with the changing environment of the web, and to work with other websites and online tools. Website: http://blog.ushahidi.com/
6) Google Android: Get inventing! This software enables anyone to start making applications for mobile phones. And it offers a platform for developers to then sell the applications to others. Website: www.android.com/
7) Afrigadget: is a website dedicated to showcasing African ingenuity. A team of bloggers and readers contribute their pictures, videos and stories from around the continent. Website: http://www.afrigadget.com


Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023


















You must be logged in to post a comment.