By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

Traditional medicines and treatments could help provide the next wave of affordable drugs and medicines for the world. But a phenomenon known as ‘bio-prospecting’ – in which global companies grab a stake in these once-free medicines – has been placing traditional medicines out of reach of Southern entrepreneurs. Pharmaceutical patents (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Patents) taken out by international drug companies are making traditional medicines expensive and inaccessible to the poor.
Indian scientists have identified more than 5000 bio-prospecting patents, worth some US $150 million, taken out by companies outside India.
Now governments in countries like India are moving to protect these recipes and the plants and animals they are made from.
The Indian government has labelled 200,000 traditional treatments as public property and free for anyone to use. These treatments are key parts of the 5000-year-old Indian health system called Ayurvedic medicine (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ayurveda) – ayur means health in Sanskrit, veda means wisdom.
“We began to ask why multinational companies were spending millions of dollars to patent treatments that so many lobbies in Europe deny work at all,” said Dr. Vinod Kumar Gupta, head of the Traditional Knowledge Digital Library, which lists in encyclopaedic detail the 200,000 treatments.
“If you can take a natural remedy and isolate the active ingredient then you just need drug trials and the marketing. Traditional medicine could herald a new age of cheap drugs,” Gupta told The Guardian..
Currently, it is very expensive to follow the Western approach to developing drugs. A so-called “blockbuster drug” can cost US $15 billion and take 15 years to bring to the market. With patents lasting 20 years, a drug company can have as little as five years to recover its development costs. This helps explain the high prices for drugs.
Unlike traditional healers in the South, multinational corporations can marshal the money, time and legal resources to file patents.
In the past, India has fought expensive and lengthy battles to revoke patents on traditional remedies. One example is the battle over the popular Indian spice turmeric powder (used for healing wounds, among other things). A patent awarded to the University of Mississippi in 1995 was successfully withdrawn after a legal battle by the Indian government.
The Indian government’s move to make traditional medicines and therapies public property promises to unleash a new wave of natural remedies and drugs and to expand the market for Southern health entrepreneurs drawing on traditional knowledge and recipes.
As the world’s economy continues to suffer, finding new ways to earn incomes and spark a whole new generation of businesses will be crucial to recovery.
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines traditional medicine as “the sum total of knowledge, skills and practices based on the theories, beliefs and experiences indigenous to different cultures that are used to maintain health, as well as to prevent, diagnose, improve or treat physical and mental illnesses.”
The importance of traditional medicines in primary health care can be seen in Asia and Africa, where its usage reaches 80 percent of the population in some countries (WHO). Herbal medicines alone are worth billions of dollars a year in sales. Examples of traditional remedies include antimalarial drugs developed from the discovery and isolation of artemisinin from Artemisia annua L., a plant used in China for almost 2000 years. In 2003, doctors found scientific evidence supporting the use of traditional Ghanaian plants to help wounds heal. Parts of the African tulip tree and the Secamone afzelli are made into pastes which are applied to wounds.
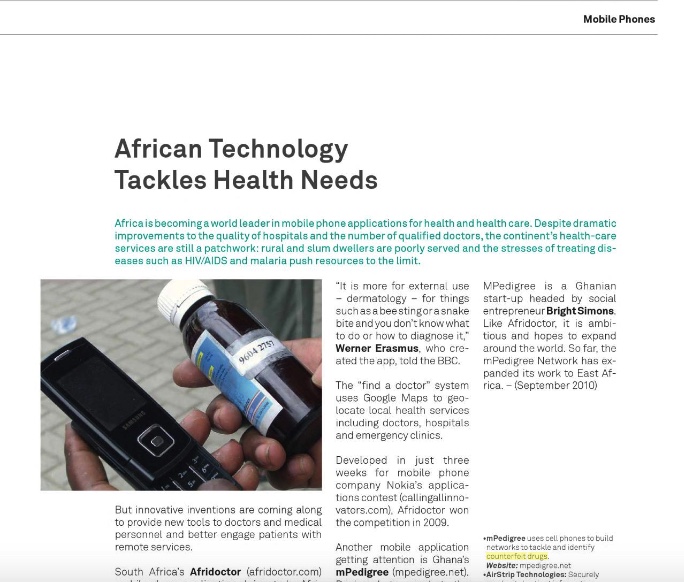
The downside of traditional medicine is the urgent need for better regulation and safety standards. While more than 100 countries have regulations for herbal medicines, counterfeit, poor quality or adulterated herbal medicines are still a major problem.
Herbal treatments are the most popular form of traditional medicine, and are highly lucrative in the international marketplace. Annual revenues in Western Europe reached US $5 billion in 2003-2004.. In China, sales of products totalled US $14 billion in 2005. Herbal medicine revenue in Brazil was US $160 million in 2007 (WHO).
One initiative is ensuring there is a solid future for traditional medicine in India. Charity Bodytree India, set up in 2004 by a group of health, human rights and education workers, addresses issues surrounding access to health care and the disappearing traditional medical practices amongst isolated indigenous communities. Bodytree has established a successful educational programme that trains young people from different indigenous communities to become community health workers and operates programmes of health education for community groups (http://www.bodytree.org/index.html).
Almost four-fifths of India’s billion people use traditional medicine and there are 430,000 Ayurvedic medical practitioners registered by the government in the country. The department overseeing the traditional medical industry, known as Ayush, has a budget of 10 billion rupees (US $260 million).
In the state of Kerala in India’s South, Ayurveda medical tourism has become a good income generator. And it is so popular in the nearby nation of Sri Lanka, hotels can have Ayurveda included in the name.
Indian entrepreneurs are drawing on increasing awareness of the importance of healthy living and rising interest in vegetarian diets – what were once holidays are now health experiences. With global obesity rates rapidly rising, along with the attended diseases like cancer and diabetes, more and more people are looking for a dramatic change to their eating and lifestyle habits to ensure long-term health. And traditional medicine has solutions.
Published: March 2009
Resources
- The Department of Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy of the Ministry of Health and Welfare, India. The website gives detailed descriptions of the practices and information on research. Website: http://indianmedicine.nic.in/
- WHO Factsheet on traditional medicines. Website: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs134/en/
- Third Global Summit on HIV/AIDS and Indigenous Knowledge in Celebration of 7th African Traditional Medicine Day, August 25-31, 2009. Website: http://www.africa-first.com/3rdglobalsummit2009/Default.aspx
- General Guidelines for Methodologies on Research and Evaluation of Traditional Medicine by the World Health Organization. Website: http://www.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Jwhozip42e/5.2.html
- UNESCO’s Open Training Platform provides a plethora of training manuals on how to set up traditional medicine businesses. Website: http://opentraining.unesco-ci.org/cgi-bin/page.cgi?g=Categories%2FHealth_and_sanitation%2FTraditional_medicine%2Findex.html;d=1
- An online shopping site based in Kerala, India offers a wide range of the Ayurvastra (healing) clothing: http://www.ayurvastraonline.com/
- Highlights from the WHO’s first Congress on Traditional Medicine in 2008. Website: http://www.who.int/medicines/areas/traditional/congress/en/index
- Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine and Herbal Technology Network: an excellent first stop for any entrepreneur, where they can find out standards and regulations and connect with education and training opportunities: www.apctt-tm.net and www.aptm.cn

Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.


This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2022






You must be logged in to post a comment.