By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

Innovators working in the global green economy could benefit from over US $450 million in investment recently pledged at the UN’s Global South-South Development Expo (GSSD Expo) held in Nairobi, Kenya.
A combination of green investors, businesses, governments and others came together at the UN Environment Programme’s (UNEP) headquarters in the Kenyan capital from 28 October to 1 November 2013 to share solutions and strike deals and partnerships.
The event represented a significant turning point in awareness of the role played by the global South’s innovators in global development and growing economies. The quantity of pledges and investment deals struck at the Expo bodes well for the future of south-south solution sharing.
Organized by the UN’s Office for South-South Cooperation in UNDP (UNOSSC) (southsouthexpo.org) and hosted by UNEP (unep.org) under the theme “Building inclusive green economies”, the Global South-South Development Expo (GSSD Expo) is the world’s biggest event for development solutions created in the South for the South.
“The theme of this year’s Expo is fitting in that Southern countries have both the opportunity and the obligation to pursue a ‘smarter’ development course than their predecessors,” said General Assembly President John Ashe.
Examples of the investment deals struck include helping to build organic fertilizer factories and constructing solar power plants in Kenya, and growing green business ventures for women in Egypt.
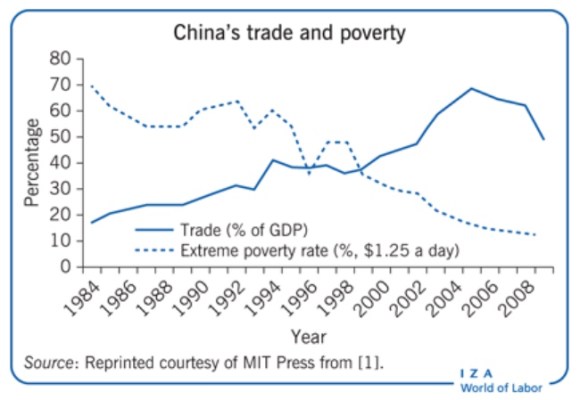
South-South cooperation is the exchange of resources, technology and knowledge between developing countries. Today, over US $5 trillion in currency reserves are held by countries of the global South. They also make up 47 per cent of global trade.
Tapping this rich resource is an unparalleled economic development opportunity and could be one of the main engines of growth in the years ahead, the Expo organizers believe.
“As so many stories that we have heard this week demonstrate, South-South Cooperation is playing a vital role in facilitating this global transition,” said UN Under-Secretary-General and UNEP Executive Director Achim Steiner.
“Not only are these local, national and regional efforts producing positive results, but they are overcoming barriers, building new partnerships, creating new finance mechanisms, generating knowledge, sharing information, providing training and capacity building in areas and sectors that are critical for a global transition to a low carbon, resource efficient and inclusive economy,” he added.
As an example of how solutions are shared and deals are struck, more than 40 companies were successfully matched and held business negotiations using the Expo’s South-South Global Assets and Technology Exchange (SS-GATE). An online match-making service bringing together innovative companies with the knowledge and funding they need to grow, the SS-GATE was able to get 148 companies to list their projects on the SS-GATE web-platform during an Expo event.
For the first time in its history, the Expo garnered a strong online presence with the help of volunteers who collaborated remotely around the world on social media. The event was so popular that it trended on Twitter in Kenya, meaning that the message of the value and growing scope of South-South cooperation reached the next generation of development practitioners, entrepreneurs, environmentalists, thinkers and leaders.
Also at the Expo, the fourth issue of Southern Innovator magazine (southerninnovator.org) had its official launch. Southern Innovator Issue 4 visits the new cities being built to tackle the challenges of a rapidly urbanizing 21st-century world. The magazine also highlights some of the solutions being devised to the challenges people face as the world becomes a majority urban place.
Some innovators are building new cities from scratch, applying the latest thinking and hard-wiring in cutting-edge information technologies and innovative environmental measures to create “smart” cities and eco-cities. Architects are designing and refining homes that are beautiful and functional, easy to build, affordable and conserve energy. Social entrepreneurs are innovating ways to create liveable and socially inclusive urban areas, often in places where planning has been scant and where incomes are very low. All the stories featured in the magazine were chosen for their focus on improving human development and for their ingenuity and fresh thinking.
Southern Innovator champions a 21st-century global innovator culture. It is being distributed through the United Nations’ network and partners and reaches some of the world’s poorest and remotest places, as well as the vibrant but stressed growing global megacities. It is hoped the magazine will inspire budding innovators with its mix of stories, essential information, facts and figures, images and graphics.
Published: November 2013
Resources
1) Global South-South Development Expo: The Global South-South Development Expo (GSSD Expo) is the FIRST EVER Expo solely from the South and for the South. It showcases successful Southern-grown development solutions (SDSs) to address the need to meet the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). Website: http://www.southsouthexpo.org/
2) Southern Innovator online story archive: Organized by theme, the story archive is a treasure trove of innovation stories and resources from the global South stretching back to 2006. Website: southerninnovator.org
3) Southern Innovator on Scribd: Archived copies of the full-color, 60-page magazine can be downloaded here. Website: http://www.scribd.com/SouthernInnovator.
4) Southern Innovator on Twitter: Catch Southern Innovator’s Tweets and keep on top of a growing global network of innovators. Follow @SouthSouth1
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.


This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2021



















You must be logged in to post a comment.