By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

With the so-called Arab Spring still unfolding across much of the Arabic-speaking world, it is easy to miss a rising new economic opportunity: The introduction of an Arabic domain name system for the Internet.
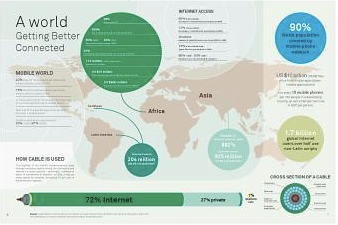
The explosion in mobile phones in the Arab world has dramatically increased the number of people who can now access the Internet. One Arabic financial website put the number of people who can now access the Internet in one way or another in the Arab world as 75 million (www.nuqudy.com). As highlighted in the 2003 Arab Human Development Report (AHDR), Arabic-speaking countries have been at a knowledge disadvantage for some time: more than 270 million citizens have access to fewer books than other languages, slower growth economies, and greater illiteracy than the faster-growing emerging economies. At the time, the AHDR found there were just 18 computers per 1,000 people compared to a global average of 78. And just 1.6 percent of Arabs had Internet access, one of the lowest ratios in the world (AHDR 2003).
Since the dawn of the Internet, Latin script has been used exclusively for top-level web domain names, the addresses that end .com, .org and so on. That has been a big obstacle for users of non-Latin script languages like Arabic. It is estimated just 10 percent of people in the Arab world speak English. Many of the resources on the Internet and its utility have been lost to these people. But by using Arabic domain names, there will be a consistency and no more guesswork.
A typical problem in Latin transliterations of Arabic is the conundrum as to either using El or Al as the prefix to a word. This problem is eliminated when Arabic is used.
The Arab world is also very mixed, including the resource-rich, cash-rich Gulf States – Kuwait, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Oman and Bahrain – and states with high rates of poverty such as Egypt, Djibouti and Yemen.
The protests and uprisings this year in Tunisia, Egypt and elsewhere – with their Facebook pages and Twitter streams – have shown that a growing group of highly Internet-savvy young people is emerging in the Arab world. But for many without the education or the resources, access to knowledge still remains weak. But armed with Internet-capable mobile phones and Arabic language domain names, rapid change is now possible.
The number of books published in Arabic is notoriously relatively low, and print runs are small. Arabic language books make up just 1.1 percent of world production.
The AHDR reports have called this knowledge deficit a direct obstacle to human development in Arab countries.
But things are changing and the rise of Arabic domain names offers the potential for an explosion in Arabic language Internet content.
In May 2010 ICANN, the world’s Internet domain authority, decided to allow top-level domains in non-Latin script. For Arabic speakers, it started this program in Egypt, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates.
As a sign of the importance of Arabic participation in future growth of the Internet, this year’s World Summit for the Information Society (WSIS) held in Geneva, Switzerland in May 2011 was sponsored by the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
A catchy domain name has many advantages. For Arabic speakers, this means they can type in Arabic domain names for websites and even do it right to left, as they do in print.
In 2009, the first Arabic domain name was grabbed by Egypt. As the Internet naming authority, the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) (www.icann.org), started to allow the registering of non-Latin script names. The domain was for the Arabic word for Egypt or “.masr”.
As an early adopter, Egypt sees it as an important part of bringing more Arabic speakers online. George Victor, from the Egyptian National Telecom Regulatory Authority, told the BBC: “We believe that this is a great step that will open new horizons for many e-services in Egypt, and it will have its direct impact, enlarging the number of online users.”
Victor believes using Arabic builds trust.
“Having a domain name in your own language is a point of having a local identity,” he said.
“When talking about Arabic domain names, we are talking about having users which are not online now. People with languages disabilities – people who are having language as a barrier to connect online.”
From now on Internet address names will be able to end with almost any word in any language, offering organizations around the world the opportunity to market their brand, products, community or cause in new and innovative ways.
The advantages of registering an Arabic domain name are numerous. They include clear improvements to business and trade: an ability to protect a trademark, better communication with Arabic customers, better Arabic-language advertising opportunities, better memorability for Arabic domain names because they will be in the Arabic language, and greater access to Arabic customers.
But there are also significant improvements to how the Internet functions in the Arabic world. Search results on Arabic search engines will be more precise with Arabic domain names; catchy, memorable domain names will be a spur to the advertising and marketing industries; and a more Arab-friendly Internet will draw in more Arabic-speaking Internet users, helping them to enjoy the fruits of this great technological advance just as speakers of other languages have.
In March 2011, the Gulf state of Qatar enthusiastically started to offer Arabic domain names.
“The launch of Qatar’s Arabic top-level domain names is a major milestone as we work to build a more digitally inclusive society,” said Dr. Hessa Al Jaber, Secretary General of the Supreme Council of Information and Communication Technology, which will manage Qatar’s Internet domain names through the Qatar Domains Registry.
“As more organizations and individuals begin adopting Arabic domain names, the Internet will literally be opened up to broad new audiences. The Arab world represents a region with enormous potential for growth both in terms of usage and the creation of new digital content, especially Arabic content.”
ICANN’s President and Chief Executive, Rod Beckstrom, sees this as a new phase for the Internet: “ICANN has opened the Internet’s naming system to unleash the global human imagination. Today’s decision respects the rights of groups to create new Top Level Domains in any language or script. We hope this allows the domain system to better serve all of mankind.”
Published: July 2011
Resources
1) Watch the ICANN educational video “Get Ready for the Next Big Thing”, explaining how domain names work and what the changes mean. Website: http://www.icann.org

https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/26/africa-to-get-own-internet-domain/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/11/berber-hip-hop-helps-re-ignite-culture-and-economy/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/02/11/egyptian-youth-turns-plastic-waste-into-fuel/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/11/innovation-cairos-green-technology-pioneers/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/21/preserving-beekeeping-livelihoods-in-morocco/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/21/social-networking-websites-a-way-out-of-poverty/
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.









This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023






















You must be logged in to post a comment.