By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

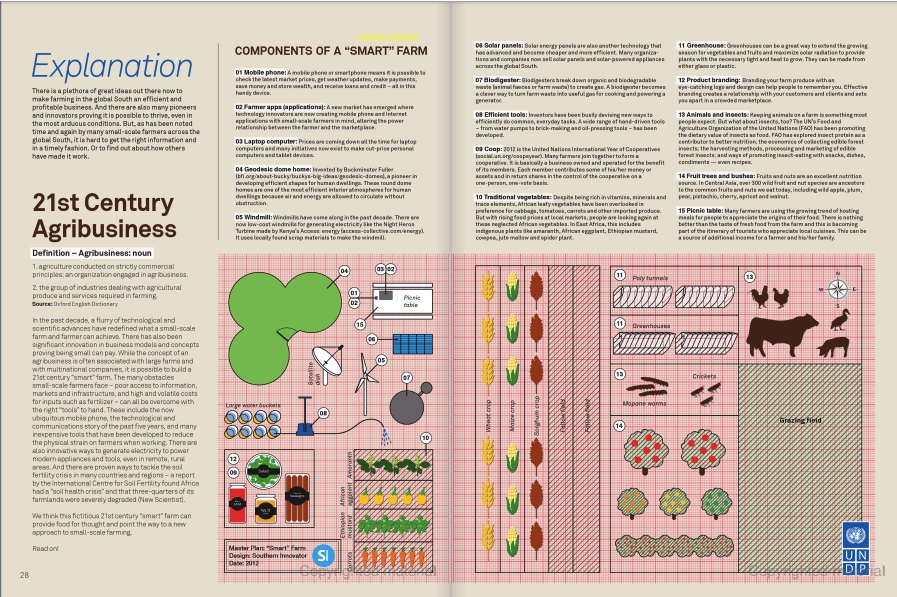
Securing energy sources that are cheap (or free) and renewable can significantly reduce the cost of living for the world’s poor. The cost of fuel for essentials such as cooking and lighting can quickly eat up household incomes.
Gaining access to an inexpensive gas source that is also renewable can help people divert their income into other things, such as education and health care, improving individuals’ well-being and helping boost wealth.
Biogas (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biogas) is fuel made from biodegradable organic material such as kitchen, animal or human waste. It can be converted into gas either by being heated or using anaerobic bacteria to break down the material and turn it into combustible methane gas (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methane).
Most biogas systems are complex and large, involving an enormous domed biodigester.
But a clever solution from Kenya, the Flexi Biogas system (biogas.co.ke), is different. It is designed to be highly portable and scalable depending on a person’s needs. The Flexi Biogas system is a pillow-shaped PVC tarpaulin, measuring 6 metres by 3 metres. It comes in two parts: a plastic digester bag on the inside and a greenhouse-like plastic tunnel on the outside. The tunnel traps heat and keeps temperatures between 25 and 36 degrees Celsius.
Subjected to the heat of the sun, the environment inside the bag encourages microbes to digest the organic material – or substrate (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_substrate_%28biology%29) as it is known, releasing biogas bubbles and inflating the bag with methane. This gas is then sent through a PVC tube that can be connected to a gas-burning appliance such as a cooking stove.
Currently, most people use the biogas for lighting and cooking but it also produces enough gas to run agricultural machinery.
The Flexi Biogas digester sits on the ground and so is easy to observe and understand.
The Flexi Biogas system is designed, built and sold by Kenya’s Biogas International, which has sold 200 of the systems since 2011. In 2012, the company partnered with IFAD – the United Nations’ International Fund for Agricultural Development (ifad.org) – to install nine systems on dairy farms in Kenya. These Flexi Biogas systems use kitchen and human waste to produce electricity for lighting and to provide Internet service.
Cows produce 15 to 30 kilograms of dung a day (IFAD). By placing 20 kilograms of fresh cow dung into a Flexi Biogas digester it is possible to produce 1,000 litres of cooking gas – enough gas for a family of five to seven people. This amount of cow dung could also produce enough gas to run a 5 horsepower engine for one hour. The engine could also be connected to a car alternator to generate electricity to run lights, a computer or a television set.
A Flexi Biogas system costs US $410, including installation by technicians and all the extras including inlet and outlet pipes and a 15 metre gas pipe.
The cost of the system increased from the first prototypes. Initially, inexpensive plastic was used for the bags and the total cost for the system was US $180. But the makers encountered a problem with durability – the systems were prone to tearing and needed to be replaced after two years. Since then, they have moved to a more expensive PVC tarpaulin bag designed to last 10 years.
The makers point out that access to high-quality plastic and rubber in Kenya is difficult and the system’s costs could be brought down if they were manufactured in China or India.
The makers argue there are several reasons why the Flexi Biogas solution is suited to Africa. One is the difficulty of securing land tenure, necessary for the building of a permanent structure like a biodigester dome. It can also be a challenge to find skilled labour and get access to complex parts such as gas pressure regulators.
In a comparison between the conventional dome biogas digester and the Flexi Biogas system, IFAD found the average cost in Kenya for a dome system was US $1,000, compared to US $410 for the Flexi Biogas system. A fixed dome takes 21 days on average to set up while a Flexi Biogas system can be set up in a day. The Flexi Biogas system also turns the substrate into biogas faster and can operate at higher temperatures. IFAD found various advantages and disadvantages to the Flexi Biogas solution: it is relatively inexpensive, lightweight (10 kilograms), very portable, quick and simple to set up, and easy to operate. The disadvantages include being costly to make, easy to steal, and a relatively short lifespan.
Weighing it all up, IFAD still concluded that “the Flexi Biogas system is an affordable solution that provides household energy while making use of waste products that would otherwise add to emissions.”
Published: December 2012
LINKS:
1) The official portal on anaerobic digestion. Website: http://www.biogas-info.co.uk/
2) REA Biogas: REA Biogas has been championing the cause of anaerobic digestion (AD) and has been the unifying force which has helped to bring the industry forward. Website: http://www.biogas.org.uk/
3) Practical Action: Various renewable energy solutions including biogas. Website: http://practicalaction.org/biogas_expertise
4) Future Biogas: Future Biogas specialise in the construction and operation of biogas plants for the UK. Website: http://www.futurebiogas.com/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/21/africa/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/08/02/african-fuel-pioneer-uses-crisis-to-innovate/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/19/agricultural-waste-generating-electricity/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/22/bio-ethanol-from-sturdy-and-once-unwanted-indian-plant/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/02/11/egyptian-youth-turns-plastic-waste-into-fuel/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/25/indian-toilet-pioneer-champions-good-ideas/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2023/03/27/pay-for-pee-keeps-indian-town-clean/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/06/23/recycling-waste-to-boost-incomes-and-opportunities/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/19/saving-water-to-make-money/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/18/successful-fuel-efficient-cookers-show-the-way/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/18/toilet-malls-make-going-better/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/08/13/turning-animal-waste-into-paper/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/09/30/turning-human-waste-to-fertilizer-an-african-solution/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/02/10/urban-farmers-gain-from-waste-water/
Follow @SouthSouth1
Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/DavidSouth1/development-challengessouthsouthsolutionsnovember2010issue
Southern Innovator Issue 1: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Q1O54YSE2BgC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 2: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ty0N969dcssC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 3: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=AQNt4YmhZagC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 4: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=9T_n2tA7l4EC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 5: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=6ILdAgAAQBAJ&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s


This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023






You must be logged in to post a comment.