By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

Zimbabwe’s turbulent descent into hyperinflation at the beginning of the 2000s – and the food crisis it caused as prices soared and purchasing power shrank – captured the world’s attention. From refugees fleeing the country to widespread hunger and poverty, the impact of hyperinflation was stark and distressing. Since the country’s economy stabilized in 2009, various signals are showing that Zimbabwe is slowly making its way back to growth and stability.
The scale of the hyperinflation is summed up by Zimbabwe’s eye-popping inflation rate. By December 2008, inflation was estimated at 6.5 quindecillion novemdecillion percent (or 65 followed by 107 zeros — 65 million googol) (Forbes Asia).
One recovery strategy is emerging in Zimbabwe’s booming eating and drinking establishments. It seems the urge to socialize and network has become the source of economic vitality where so much else has been damaged.
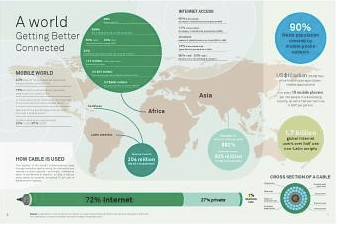
The proliferation of coffee shops with wi-fi (wireless internet access) (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wi-Fi) has spawned a new, connected business culture that is flexible and entrepreneurial.
Zimbabwe’s unity government was formed in September 2008. By the beginning of 2009, the government relented on the crippling hyperinflation and allowed business to be conducted in the US dollar. This made it possible to save again and do business with greater predictability. At this time, the country had the world’s highest inflation rate and the central bank printed a 100 trillion Zimbabwe dollar note.
The economic result of greater stability has been new shopping malls opening and a boom in new eating and drinking establishments.
During the hyperinflation, eating out was the last thing on most people’s minds. Just surviving was the paramount daily task.
In the capital, Harare (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Harare), the shopping mall Sam Levy’s Village (http://samlevysvillage.com), in the prosperous Borrowdale area of the northern suburbs, is full of thriving coffee shops, restaurants and pubs.
Outside of the wealthy enclaves, coffee shops have sprung up in the city’s art gallery, in sports clubs and a local supermarket chain.
While the coffees are still expensive relative to local wages, the Zimbabwe Online Hotspots (ZOL) (http://www.zol.co.zw) in the coffee shops have proved a big attraction. Most people in Zimbabwe have unreliable or non-existent electricity or, if lucky, poor-quality phone and internet dial-up in their homes.
ZOL Hotspots typically offer the first half hour of internet use for free. To surf longer, users must buy a voucher.
The damage done to the economy from hyperinflation and the political crisis means the country is still on the mend. But people have now resorted to what they call “networking,” according to Bryony Rheam in the Daily Telegraph newspaper. The functioning economy is all about making deals. And coffee shops with wi-fi are the perfect place to meet with a potential business partner.
But while the coffee shops are buzzing with people doing business, the proprietors still need to work out how to make better profits. Sales are still poor as people are mostly fixated on the wi-fi. One owner told the Telegraph: “We need to start charging people who sit here all day surfing the net.”
It is the restaurants who seem to be enjoying the boost in incomes and better spirits after the economic troubles. Zimbabwe’s black middle class are enjoying big occasions and celebrating with friends and family in restaurants.
“We went without for so long, that a lot of people almost see it as their right to spend money on eating out,” one patron told the Telegraph.
More good news has come from outside investors as well: Amstel Securities NV (http://www.amstelsec.com), based in Amsterdam, Netherlands calls Zimbabwe’s economy “the final frontier market in Africa”. It believes the country has the potential to grow its GDP (gross domestic product) to US $12 billion by 2015. The International Monetary Fund says the economy jumped from US $4.4 billion in 2009 to US $9 billion now.
In Amstel Securities’ report, it pegs the dollarization of the economy as the reason for stability: “These improvements have made Zimbabwe a much more vibrant economy with good further recovery potential.”
And these good vibes are contagious: it has been reported that the American hamburger chain McDonald’s is revisiting the idea of setting up in Zimbabwe. McDonald’s is currently present in a handful of African countries: South Africa has 132 restaurants.
Published: September 2010
Resources
- My Zimbabweinfo.com: A web portal packed with travel and services information on Zimbabwe. Website: http://zimbabwe.mydestinationinfo.com/en/restaurants-in-harare
- When Money Dies: The Nightmare of the Weimar Hyperinflation by Adam Ferguson. Website: http://www.amazon.co.uk/When-Money-Dies-Nightmare-Hyper-Inflation/dp/1906964440
- A guide to setting up wireless internet ‘hot spots’. Website: http://wireless.navigator.co.uk/hotspots.htm

Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.





This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023

















You must be logged in to post a comment.