By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

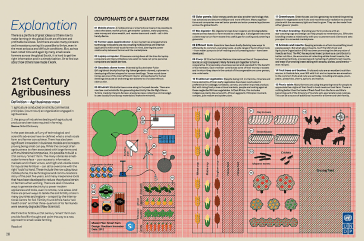
As the world’s population continues to grow – surpassing 9 billion people by 2050, the United Nations estimates – and more and more people move to urban areas, producing enough food to feed this population will be one of the biggest economic challenges and opportunities in the global South.
Africa, a continent undergoing significant economic change, has yet to fully realize its potential as a producer of agricultural products to feed itself and the world. Africa currently has a labour-intensive but very inefficient agriculture system. While many Africans either make their living in agriculture or engage in subsistence farming for survival, much of the continent’s farming is inefficient and fails to make the most of the continent’s rich resources and potential.
A new World Bank report, Growing Africa: Unlocking the Potential of Agribusiness (http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTAFRICA/Resources/africa-agribusiness-report-2013.pdf), argues that Africa could have a trillion-dollar agriculture market by 2030.
What will need to change to make this happen? African farms will need greater access to capital, as well as more investment in infrastructure and better irrigation. All of these elements will need to dramatically improve if Africa is going to compete effectively in global markets.
The report urges greater cooperation between governments and agribusinesses, farmers and consumers and for all parties to recognize that the continent is being rapidly urbanized, changing the way food is grown, sourced and distributed.
It says Africa’s farmers and agribusinesses require more capital, steady supplies of electricity, better technology and irrigated land. All these resources then need to be applied to the growing of high-value, nutritious foods.
At present, agriculture, farmers and agribusinesses make up almost 50 per cent of Africa’s economic activity, and the continent’s food system is worth an estimated US $313 billion a year (World Bank). But the report believes this could triple if governments and business leaders adopted radically different policies.
“The time has come for making African agriculture and agribusiness a catalyst for ending poverty,” said Makhtar Diop, the World Bank Vice President for Africa. “We cannot overstate the importance of agriculture to Africa’s determination to maintain and boost its high growth rates, create more jobs, significantly reduce poverty, and grow enough cheap, nutritious food to feed its families, export its surplus crops, while safeguarding the continent’s environment.”
The report addresses the problems African agriculture is currently experiencing: slow yield growth for major food crops, slowing research spending, degraded land, water scarcity, and climate change. It looks at solutions to allow Africa to tackle these problems and seize the opportunity to significantly increase its food and agricultural exports. Africa can more than meet its own needs and meet the world’s needs too, the report argues.
But what can be done? At present, 50 per cent of the world’s uncultivated land suitable for growing food resides in Africa. This works out to 450 million hectares of land that is neither forested, protected nor densely populated – all could be available for growing food.
The report also found Africa is using just 2 per cent of its renewable water resources while the rest of the world averages 5 per cent. African harvests currently do not yield anything close to what is possible. Another weakness is waste from post-harvest losses, averaging 15 to 20 per cent for cereals, and even more for perishable foods, because of poor storage and farm infrastructure.
Areas the report recommends farmers and agribusinesses should focus on include fast-growing markets for rice, maize, soybeans, sugar, palm oil, biofuel and feedstock. In sub-Saharan Africa, the focus should be on rice, feed grains, poultry, dairy, vegetable oils, horticulture and processed foods for the domestic market. And there are also good examples to follow by studying the ways Latin America and Southeast Asia used world markets to boost income and profits.
Agribusiness enterprises looking to purchase more land to expand the number of hectares under cultivation are urged to act ethically and not to threaten existing people’s livelihoods or violate local users’ rights. This includes consulting with locals and paying fair market price for land bought.
Rice is one crop that needs attention. Significant quantities of rice are imported and consumed in Africa. Half the rice eaten is imported, costing around US $3.5 billion a year (World Bank). Big importers include Ghana and Senegal – both countries singled out in the report for needing to improve their domestic rice production and quality.
Another food staple needing attention is maize (corn). A daily food staple for many Africans, it takes up 14 per cent of crop lands on the continent. While most Zambians get half their calories from maize, Zambia is currently unable to export maize at a cost comparable to market leader Thailand – Zambian maize costs one-third more. Zambia was singled out as needing to raise yields, reduce costs, and remove disincentives for the private sector in markets and trade.
“Improving Africa’s agriculture and agribusiness sectors means higher incomes and more jobs. It also allows Africa to compete globally. Today, Brazil, Indonesia and Thailand each export more food products than all of sub-Saharan Africa combined. This must change,” said Jamal Saghir, the World Bank’s Director for Sustainable Development in the Africa Region.
How to make the most of this opportunity?
One innovative idea coming out of Africa comes from the mega-brewer SABMiller (sabmiller.com). As a sign of confidence in the continent’s growing economies, the brewer has pledged to slash its beer prices and use more African-grown grains – a boost to local farmers – and to start a campaign of opening new breweries for the next three years. Countries targeted include Ghana, Nigeria, Mozambique and Zambia.
“African farmers and businesses must be empowered through good policies, increased public and private investments and strong public-private partnerships,” according to Gaiv Tata, World Bank director for Financial and Private Sector Development in Africa. “A strong agribusiness sector is vital for Africa’s economic future.”
Published: May 2013
Resources
1) Southern Innovator Magazine Issue 3: Agribusiness and Food Security: Southern Innovator’s third issue finds innovators transforming agribusiness and boosting food security. Website: http://www.scribd.com/doc/106055665/Southern-Innovator-Magazine-Issue-3-Agribusiness-and-Food-Security
2) The New Harvest: Agricultural Innovation in Africa by Calestous Juma. Website: http://belfercenter.ksg.harvard.edu/publication/20504/new_harvest.html
3) Growing Africa: Unlocking the Potential of Agribusiness. Website: http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTAFRICA/Resources/africa-agribusiness-report-2013.pdf
4) Edible Insects: future prospects for food and feed security, Publisher: FAO. Website: http://www.un.org/apps/news/story.asp?NewsID=44886
5) Six-legged livestock: edible insect farming, collecting and marketing in Thailand, Publisher: FAO. Website: http://www.fao.org/asiapacific/rap/home/news/detail/en/?news_uid=176061

London Edit
31 July 2013

https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2020/12/14/african-farming-wisdom-now-scientifically-proven/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/21/agribusiness-food-security/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/08/14/brazil-preserves-family-farms-keeping-food-local/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/10/cheap-farming-kit-hopes-to-help-more-become-farmers/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/02/10/food-inflation-ways-to-fight-it/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/05/04/insects-can-help-in-food-crisis/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/23/putting-worms-to-work/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/03/05/southern-innovator-issue-3/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/14/staple-foods-are-becoming-more-secure-in-the-south/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/03/20/texting-for-cheaper-marketplace-food-with-sokotext/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/11/urban-farming-to-tackle-global-food-crisis/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/18/woman-wants-african-farming-to-be-cool/
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.






This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023










You must be logged in to post a comment.