By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

Ethiopia’s bustling capital, Addis Ababa, is experiencing a building and business boom. Foreign investors and Ethiopia’s entrepreneurial and widespread global diaspora are investing again in the country. But Ethiopia still relies for most of its foreign currency wealth on exports of unprocessed coffee beans and leather hides — a model that leaves the bulk of the profits made outside of Ethiopia.
But one shoe company provides an example of a home-grown business that is finding success in the international marketplace, while repatriating most of the profits for its goods back to Ethiopia, creating jobs and local wealth.
Ethiopia’s economy is mostly dependent on agriculture, which accounts for 60 percent of exports and 80 percent of employment (CIA World Factbook). The country has a tiny private sector and high youth unemployment. It is difficult to find funding for small businesses. Yet, because of the high population growth, the country needs to create more jobs.
The Economist magazine has forecast Ethiopia’s economy will grow by 7 percent in 2010, becoming the fifth fastest growing economy in the world, and on course to surpass Kenya to become East Africa’s biggest economy. While this sounds impressive, the country has to run hard to create enough jobs to meet its growing population and still faces significant food security problems.
One company, soleRebels, is combining a clever twist on a local tradition – recycling rubber from old truck tires into shoes, locally known as selate shoes – with sophisticated design concepts and high quality craftsmanship to make a global footwear hit.
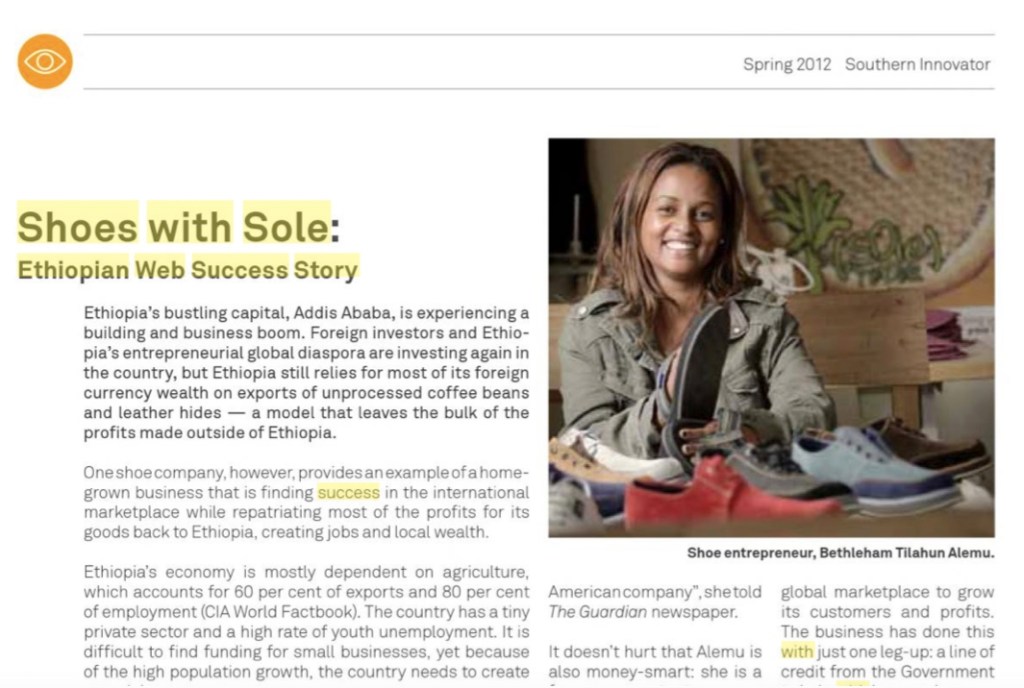
Co-founder and managing director Bethleham Tilahun Alemu, a 30-year-old African web-vending entrepreneur, has turned this local craft into a global fashion design hit by adding colourful cotton and leather uppers to the tire shoes. The recycled rubber shoes come in many styles: from handmade flip-flops to boat shoes, loafers, and athletic trainers resembling the popular American sports shoe, Converse (http://www.converse.com/).
SoleRebels’ (http://solerebelsfootwear.weebly.com/index.html) shoe factory is on the outskirts of Addis Ababa in the historic village of Zenabework. Despite its location, it is reaching the international markets through online retailers like Amazon.com. Shipments take between three and five days to arrive in the United States.
And the secret to this small start-up’s success? Apart from great shoes and funky design, Alemu puts it down to this: “We are sitting in Addis Ababa but acting like an American company,” she told The Guardian newspaper.
It doesn’t hurt that Alemu is also money-smart: she is a former accountant.
Started five years ago, soleRebels now employs 45 full-time staff making 500 pairs of shoes a day. The shoes cost between US $33 and US $64. They are also being sold in Japan and the United Kingdom on Amazon’s shoe-selling website, http://www.javari.co.uk.
In 2010, Alemu hopes soleRebels will make US $481,000. But soleRebels has an even more ambitious goal: to become “the Timberland or Sketchers of Africa.”
Timberland (http://www.timberland.com/home/index.jsp), an American shoe and boot maker, has been a pioneer in high-quality leather footwear, breaking new ground in adopting green manufacturing processes and exploiting the power of the web by allowing customers to customise their footwear.
SoleRebels has cleverly exploited the advantages of the global marketplace to grow its customers and profits. The business has done this with just one leg-up: a line of credit from the government to help with large orders. With 6.2 million people out of a population of 80 million needing food aid, Ethiopia is still highly dependent on international aid. But Alemu is showing there is a way to build a sustainable successful business.
Inspiration for Alemu came about when she was thinking what Ethiopian product could be produced in a sustainable way. She remembered the sandals worn in the country.
“Recycling is a way of life here – you don’t throw things away that you can use again and again,” she said. “I wanted to build on that idea.”
Ethiopian shoe makers have had a difficult time in recent years, trying to compete with cheaper Chinese imports. But rather than just trying to come up with a shoe that was even cheaper than the Chinese ones, soleRebels decided to build a business selling shoes to the more lucrative export market.
Alemu reasoned that good design would attract a higher price. She did research on the internet to find out which designs worked well and what were the latest trends in footwear.
This research formed the basis of her range of shoes, which have catchy names like Class Act or Gruuv Thong. The sandals and flip-flops are either cotton-covered or leather covered. The Urban Runner shoe sells best and is inspired by the Converse All Star sneaker.
SoleRebels has a regular supplier of old truck tires and inner tubes and has women weave and dye the cotton, jute and hemp uppers for the shoes. Almost all materials are locally sourced. Old army uniforms are cannibalized for their camouflage pattern.
SoleRebels has also been canny in seeking Fair Trade certification (http://www.fairtrade.org.uk) to help with marketing and selling the shoes.
To increase the market for the shoes, Alemu bombarded American retailers with emails and shoe samples to pique their interest. Because of the U.S. African Growth and Opportunity Act (http://www.agoa.gov), soleRebels’ shoes can be imported into the United States duty-free: a big price advantage in the U.S. marketplace which has helped grab the interest of retailers like Whole Foods and Urban Outfitters.
This interest soon snowballed, and people were placing orders through the soleRebels website (http://solerebelsfootwear.weebly.com/index.html). Orders come by courier from Ethiopia in about a week to the United States.
With all this interest building, Amazon, the leviathan online retailer, decided to become a customer for the shoes. Online retailing has been a huge boost to the growth of soleRebels. According to Alemu, it has enabled the company “to understand the market needs and demands in real time” — a huge advantage to a start-up company far away from its markets.
There is another advantage to using the web to grow a business: it has enabled soleRebels to take greater control of the whole process. The company negotiates directly with retailers, handling orders and credit collection, and this makes sure most of the profits of the business return to Ethiopia.
Making soleRebels quickly profitable has been a benefit to its workers. Starters at the company make US $1.92 a day, while experienced shoe-makers earn US $11 a day (a good wage in Ethiopia).
“In Ethiopia we have become used to taking money from the West, to always getting help,” Alemu told the Guardian. “That does not make for a sustainable economy. We need to solve our own problems.” And what does success enable them to do? SoleRebels are now building a solar-powered factory to replace their current workshop. And there is a steely pride in the firm’s success: “People buy soleRebels because they are good, not just because they are green or from Ethiopia,” Alemu said. “Our product speaks for itself.”
Published: January 2010
Resources
1) The online service CafePress is a specially designed one-stop shop that lets entrepreneurs upload their designs, and then sell them via their online payment and worldwide shipping service. Website: http://www.cafepress.com/cp/info/sell/
2) Once inspired to get into the global fashion business, check out this business website for all the latest news, jobs and events. Website: http://us.fashionmag.com/news/index.php
3) iFashion: This web portal run from South Africa has all the latest business news on fashion in Africa and profiles of up-and-coming designers. Website: http://www.ifashion.co.za/index.php?option=com_frontpage&Itemid=1
4) The red dot logo stands for belonging to the best in design and business. The red dot is an internationally recognised quality label for excellent design that is aimed at all those who would like to improve their business activities with the help of design. Website: http://www.red-dot.de
5) Dutch Design in Development: As a matchmaker, DDiD puts together European clients, Dutch designers and small and medium-sized enterprises in developing countries. The designers share their knowledge of European consumer tastes, product development, design and quality standards. Website: http://www.ddid.nl
6) ShopAfrica53: Pledging in its motto to reach “every African nook and cranny,” ShopAfrica53is an online shopping portal similar to famous brands like Amazon or eBay, but focused entirely on giving African traders the ability to sell across the continent and to the world online. Website: http://www.shopafrica53.com/
7) Havianas: A Brazilian global fashion success with its rubber flip flops. Website: http://www.havaianas.com/
8) Arise Africa Fashion Week: The place to be seen and to see. Website: http://www.africanfashioninternational.com/africaFashionWeek/
As featured in Southern Innovator Issue 2: Youth and Entrepreneurship. Designed and laid out in Iceland using 100% renewable energy.




https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/19/african-culture-as-big-business/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/02/09/african-fashions-growing-global-marketplace-profile/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/01/05/afropolitan-african-fashion-scene-bursting-with-energy/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/01/25/creating-green-fashion-in-china/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/09/fashion-closes-gap-between-catwalk-and-crafts/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/16/favela-fashion-brings-women-work/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/06/27/new-swimwear-for-plus-size-women-in-brazil/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2020/11/24/too-black/

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023











You must be logged in to post a comment.