Editor and Writer: David South
Researcher: G. Enkhtungalug
Publisher: UNDP Mongolia Communications Office
Published: February 1999
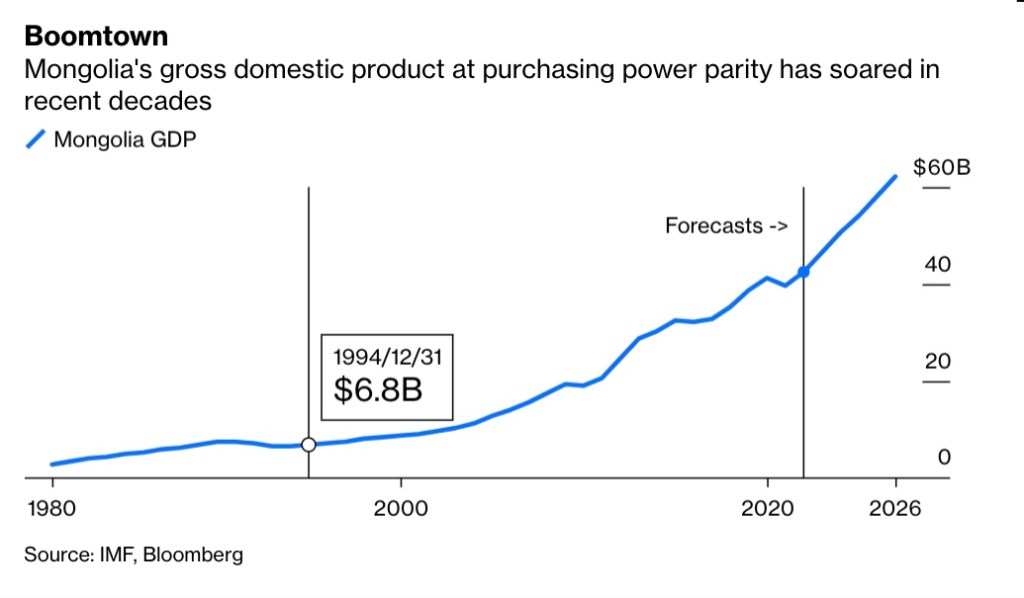
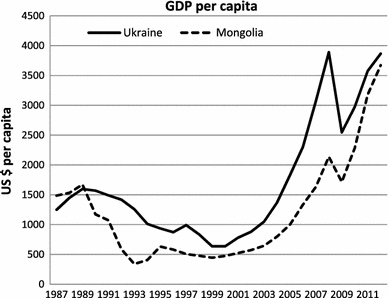
Background: Mongolia Update – Coverage of 1998 Political Changes was a one-off special edition of Mongolia Update to help explain a politically turbulent year where three governments and three prime ministers came and went. At the time, Mongolia was in the grips of a severe crisis, called one of “the biggest peacetime economic collapses ever”. By 2012, Mongolia was called the “fastest growing economy in the world”. It is proof the foundations for Mongolia’s recovery from crisis were laid in the late 1990s. The success of the peaceful transition stands in stark contrast to many other international interventions post-2001.

This is an unofficial publication of UNDP. Views presented in this document do not necessarily reflect those of UNDP. Mongolia Update is provided as a service to those who are interested in the rapid changes taking place in today’s Mongolia. A note about Mongolia Update: The Mongolia Update has proven to be one of the more popular documents produced by the UNDP Mongolia office. Since the autumn of 1997 UNDP has been able to offer two more frequently updated sources of information: the UNDP homepage and our monthly newsletter, the Blue Sky Bulletin (available from our office if you are not already receiving it). Please use the United Nations Homepage at http://www.un-mongolia.mn to keep abreast of the latest political, economic and social developments in Mongolia. Mongolia Update is an unofficial document of UNDP and is designed to periodically keep our partners outside of Ulaanbaatar apprised of issues in the country.
A year of political divisionsWho is who in the cabinet
A government of technocrats
Background — a year of political divisions
Divisions in the ruling Democratic Coalition Government in 1998 led to the fall and rise of three governments and three prime ministers. From the beginning of 1998 cracks within the Coalition intensified. A number of Democrats were dissatisfied with the system whereby the Prime Minister and the Cabinet were not parliamentarians, but “experts” appointed from outside and perceived to be aloof from Parliament. On January 15, 1998, after several weeks of wrangling Parliament ruled that under the Mongolian constitution MPs could serve as Cabinet ministers. It was to prove a fateful decision for the year-and-a-half old M. Enkhsaikhan Government.
A faction within the Coalition Government became more vociferous, with its complaints that the Democrat’s election promises would not be fulfilled without better coordination between the Government and the Parliament. Things came to a head when the General Council of the Mongolian National Democratic Party (MNDP) called for the resignation of its own Government. The move was led by the 35-year-old Speaker of the Parliament and MNDP caucus leader Ts. Elbegdorj – a natural Prime Minister in a Government of MPs. After a joint meeting of the ruling councils of the Mongolian Social Democratic Party (MSDP) and the MNDP, Prime Minister Enkhsaikhan handed in his resignation to Mongolian People’s Revolutionary Party (MPRP) President Bagabandi. The new Prime Minister, Ts. Elbegdorj, was sworn into office on April 23, vowing to chart the same economic course as his predecessor. While trying to form his Cabinet, Elbegdorj quickly ran into trouble.
The opposition MPRP was emboldened, exploiting the fissures in the Democratic Coalition. They started to launch attacks against the new Government. Elbegdorj’s attempts at forming a Cabinet were delayed as one candidate after another was rejected.
The Cabinet was not composed until May 28, when 28-year-old CH. Saikhanbileg became Education Minister – the fifth nominee put forward for the post. The new Government faced an opposition boycott of Parliament by the beginning of June, in the wake of the merging of a state bank with a private bank amidst charges of conflict of interest. On July 25 Ts. Elbegdorj and his entire Cabinet resigned after losing a no-confidence vote in Parliament. The Elbegdorj cabinet continued to work as an acting Government. The murder of prominent democrat and minister of infrastructure S. Zorig shocked the nation October 2. Poised to become a candidate for Prime Minister, Zorig was axed to death in his apartment by two assailants. The crime remains unsolved and grabbed international headlines in what had been seen as the most peaceful country making the transition from communism to democracy. In November the Constitutional Court ruled MPs holding Cabinet posts as unconstitutional. This effectively reversed the aforementioned Parliament decision of January 15, 1998. Throughout the year opinion polls showed a growing weariness and disillusionment creeping into the body politic over the political indecision.
By December a compromise Prime Minister was found, in the form of the mayor of the capital city, Ulaanbaatar. On December 9 Prime Minister Narantsatsralt took office. As 1998 turned into 1999, Narantsatralt was still trying to have his Cabinet approved by both the Parliament and the President.
External economic turmoil started to have its affect on Mongolia in 1998. Many thought the country could ride out the Asian crisis unscathed, but Prime Minister Ts. Elbegdorj admitted in June it was unavoidable. Copper prices, Mongolia’s largest foreign currency earner continued to plummet to record lows. Prices for cashmere and gold, major exports for Mongolia, also declined. The picture for the domestic economy had some bright spots in 1998, with inflation under control and an expansion in the informal service sectors. The Government’s Green Revolution campaign was able to significantly boost the production of vegetables by encouraging home gardening. The economy was still supported by foreign aid, which totaled US $205 million in commitments for the year.
Instability in Russia has also had an impact on Mongolia. For example, in May Russian coal miners blocked the Trans-Siberian train that passes through the capital Ulaanbaatar on its way to China. In August a severe benzene shortage prompted the reintroduction of rationing. At its worst all gas supplies for the country were pulled back to the capital, leaving many stranded and unable to drive cars and run gas-powered electricity generators. The delays were due to job actions by Russian workers. Russia accounts for 30 per cent of Mongolia’s imports and 13.5 per cent of its exports. On the plus side, foodstuffs from Russia became cheaper with the decline of the rouble.
Who is who in the Cabinet
Prime Minister R.Amarjargal, 38 year old Moscow educated economist. He graduated from Economic Institute of Moscow as an economist and a teacher in 1982 and earned a master’s degree at Bradford University in 1994-1995.
1982-1983, he was an instructor in Mongolian Trade Union, 1983-1990, he worked as a teacher in Military Institute, 1991-1996 has served as Director of the Economics College. He was a popular Foreign Relations Minister before resigning with the entire cabinet on July 24, 1998. A member of MNDP, he speaks fluent Russian and English.
Finance Minister Yansangiin Ochirsukh. Born in Ulaanbaatar, economist Ochirsukh graduated from the Mongolian National University and did postgraduate work at Columbia University in the United States. He worked as a lecturer and researcher at the University before moving to the Mongol Bank, where since 1997 he has been in charge of foreign exchange and reserve policy. A member of the Mongolian Social Democratic Party, he speaks Russian, English and Chinese.
Minister of External Relations Nyamosoriin Tuya, 40, was born in 1958 in Ulaanbaatar. Studied in the Institute of External Relations in Moscow, Russia in international journalism. From 1984 to1985 she studied French culture and civilisation at the Sorbon University and did a Masters degree on the ” Theory of Democracy” at Leeds University, England. Ms.Tuya speaks English and French. Married with two sons and a girl, she worked as editor of the foreign programming service of Mongolian Radio. After 1996, she was working as Head of the Department for Common Policy at the Ministry of External Relations.
Minister of Environment Sonomtserengiin Mendsaikhan, 39, was born in Ulaanbaatar, and completed degrees at the Mongolian State University and the State University of Irkutsk, Russia in mathematics. S.Mendsaikhan speaks German and Russian. Married, he has a daughter. Started his career as a math teacher at an Ulaanbaatar school, he also worked as a lecturer at the Mongolian State University and later become general secretary of the Social-Democratic Party. From 1992 to1993 he worked as a manager in the Unuudur (Today) private newspaper. From1993 to 1997 he worked as a private company director, and in 1997 he was assigned as advisor to the Parliament’s Speaker.
Minister of Defence Sh.Tuvdendorj, 32, graduated from the Army Academy of Mongolia and the Otgontenger Language School. He worked as an army officer, technician and laboratory engineer at the State Telecommunications Utilisation Committee. He started a political career in 1994, working as secretary in charge of local affairs. In 1997, he was elected as general secretary of the Mongolian National Revolutionary party.
Minister of Agriculture Choinzongiin Sodnomtseren, 46, was born in Ulaanbaatar and is married with three children.After attending Mongolian State Agricultural University, he acquired a Ph.D. in Saint Petersburg, Russia. He also has a Ph.D. degree in veterinarian sciences.
While spending many years of his career on research studies, he worked as a lecturer at the State agricultural University. Sodnomtseren became later Principal and Rector of the State Agricultural University.
Minister of Health and Social Welfare Sodoviin Sonin. Born in Ulaanbaatar in 1956, S.Sonin graduated from the Medical University of Irkutsk and Mongolia’s State Administration and Management Development Institute. A doctor and professor of medicine, he has taught surgery at the Mongolian Medical University, worked at the Central Clinical Hospital and served as a department chair at the Ministry of Health and Social Welfare. Since 1991 he has headed the Asian Development Bank-backed Health Sector Development project. Sonin, who speaks Russian and English, does not belong to any political party.
Minister of Infrastructure, Gavaagiin Bathuu, 39, born in Hujirt county of Uvurhangai province. Married with two sons and a daughter, he graduated from the Economics Institute of Harikof, Russia as an auto engineer and economist. He speaks Russian and English. He started his career as a repairman and dispatcher at the state auto-engineering company.From 1986 to 1992, he worked at the Ministry of Infrastructure as an officer and senior officer and from 1992 to 1996 he worked as Director of Shunklai Company. Since1996 he was working as a head of the Department for Road and Transportation at the Ministry of Infrastructure.
Minister of Justice, Logiin Tsog, 47, was born in Ulaanbaatar. He graduated from the State University in Irkutsk, and from the Social Science Academy in Russia. A lawyer with high education in politics, he speaks Russian and English. He worked as the prosecutor for the department at the Ministry of Justice. From 1988 to 1989, he worked as inspector at the Mongolian Revolutionary Party’s Inspection Committee. From 1990 to 1991, he was assigned as the Head of the Standing Committee of the State Baga Hural (parliament of that time) on legal issues. From 1991 to 1996 he was general director of the “Golden Button” Co. Ltd and in 1996 he was elected as general secretary
Minister of Enlightenment A.Battur was born in 1965 in Hovd aimag. Battur is a career diplomat who graduated from Russia’s Institute for International Affairs and completed a postgraduate course at France’s Institute for International Affairs. He worked as an attaché in the Foreign Ministry between 1989 and 1992, and spent 1992 to 1996 as the cultural attaché at the Mongolian Embassy in France-where he also worked with UNESCO- before returning to senior administrative positions at the Ministry in 1996.
A member of the Mongolian National Democratic Party, he speaks English, French and Russian and is married with two children.
A government of technocrats
By January 15, 1999 Mongolia had its first complete Government in six months. All nine members of the Mongolian Cabinet have been approved and appointed. Like Prime Minister Narantsatsralt, they are not Members of Parliament. Since all nine Cabinet Ministers were chosen for their experience, many expect a more stable course to be charted for the remainder of the Democratic Coalition’s term in office (until 2000). However, the new Government might experience the same sort of complaints the Enkhsaikhan Government received, when Parliament accused those ministers of being aloof. It is also unclear if the MPRP will continue to offer a vigorous opposition. For the time being its seems the political forces have exhausted themselves and there is a genuine desire for stability in 1999. The new Government is expected to follow the same reform directions of the two previous Democratic Coalition Governments and details will emerge over the coming weeks.
Further explore this turbulent period in Mongolia’s history here: Wild East 17 Years Later | 2000 – 2017



https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2023/01/09/mongolia-update-1998/
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2018

























You must be logged in to post a comment.