By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

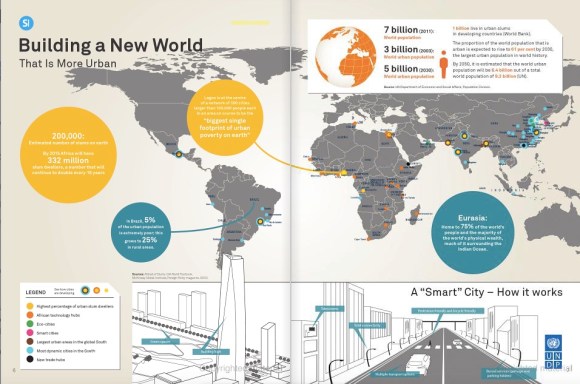
As cities in the global South grow ever larger, their often-chaotic evolution can create sprawling urban mazes that would confuse even the brightest brains.
Streets can be unnamed, unnumbered, twisty, full of dead ends and alleys. Informal settlements can pop up within weeks, whole neighbourhoods are razed to the ground and replaced by gleaming office buildings and apartments within months. Some countries experience political instability and conflict, disrupting daily life and making planning difficult. All this chaos makes business and travel more inefficient, especially to visiting businesspeople looking to trade or tourists simply wanting to look around.
When a city fails to communicate its treasures, something is lost for both parties: the city’s businesses lose valuable custom and the visitor or resident fails to grasp what is on offer. How will you find the restaurant you want, or that shop with the just-right fashions?
Beirut is a city that has had its ups and downs. Once called “the Paris of the Middle East” for its beauty and cosmopolitan atmosphere, it descended into decades of civil war and unrest from 1975, most recently in 2006 it had a war with Israel. Its residents have grown used to a city of turmoil and rapid change. They also have grown used to a city that people navigate by landmarks rather than street names.
Bahi Ghubril grew fed up with the frustration of having to always ask people for directions to get around the city, or getting stuck behind drivers begging pedestrians for directions.
Inspired by London’s famous A-Z (http://www.a-zmaps.co.uk), he researched and launched the Zawarib Beirut Road Atlas in 2005 (http://twitter.com/#!/zawaribworld) and (http://www.facebook.com/zawarib).
It is part of a new trend across the global South: people using the slew of new information technologies and online resources to map and discover their neighbourhoods and cities. In turn, this is fuelling economic growth as people can find businesses and promote themselves to buyers and customers.
It took Ghubril two years to put together the first guide, gathering street images from satellite photos and then combining them with information collected on foot and from local mayors and cartographers.
“The project was born from a need to organise the city,” he told Monocle magazine, “but also as a socio-political project to open up the city to its residents and visitors.”
As an entrepreneur, Ghubril had no previous experience in publishing. He has been an actor and worked in finance.
During the research for the guide, Ghubril developed a rich knowledge of the city’s structure, its bureaucracy and how people really live their lives. His willingness to do this hard work is paying off.
Zawarib Beirut – which translates as Beirut Alleys – has successfully expanded into editions covering nearby cities, a pocket version, eight versions colourfully decorated by local artists, and the first Beirut bus map.
The service has a database including thousands of street names, landmarks, sectors and districts within the 34 municipal regions making up Greater Beirut. It includes useful phone numbers, car parks and a bus map. During holidays, like the Muslim holy month of Ramadan, it publishes a map of all of Beirut’s mosques.
Ghubril promotes the guide directly to the city’s residents. Wearing blue and black t-shirts asking “Lost? ask me,” young women help to distribute the guide on the streets of Beirut.
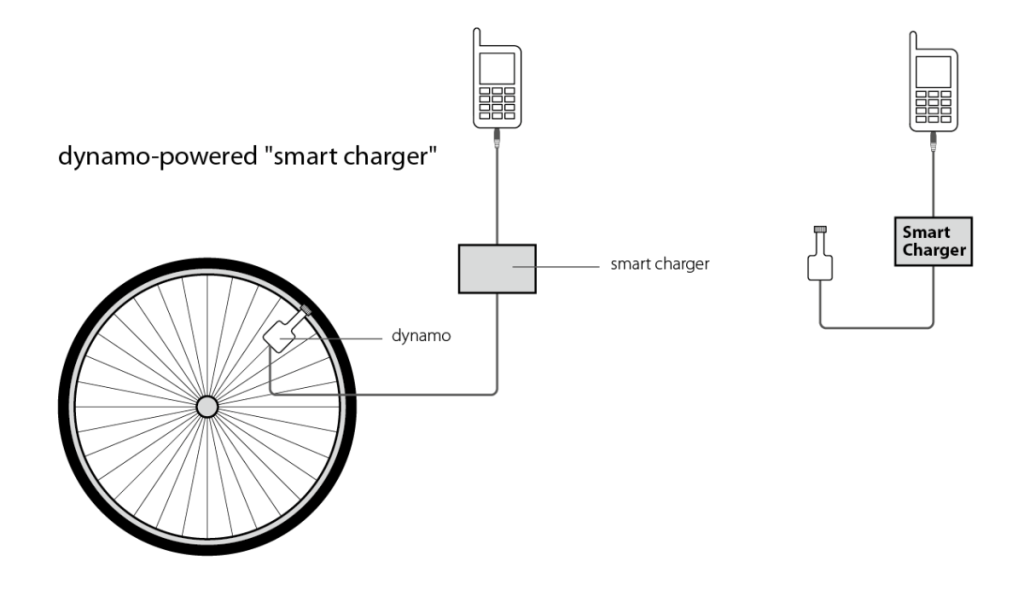
Other mapping projects depend on the mobile phones that are more and more part of daily life in the South’s slums – even for the poorest people. With the spread of mobile phones, it is becoming possible to develop a digital picture of a slum area and map its needs and population. It has become possible to undertake digital mapping initiatives to truly find out who is where and what is actually going on.
An NGO called Map Kibera (http://www.mapkibera.org) is working on an ambitious project to digitally map Africa’s largest slum, Kibera in Nairobi, Kenya.
The Map Kibera project uses an open-source software programme, OpenStreetMap (http://www.openstreetmap.org), to allow users to edit and add information as it is gathered. This information is then free to use by anybody wanting to grasp what is actually happening in Kibera: residents, NGOs, private companies and government officials.
It will literally put Kibera on Kenya’s map.
In Brazil, an NGO called Rede Jovem (http://www.redejovem.org.br) is deploying youths armed with GPS (global positioning system)-equipped (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Global_Positioning_System) mobile phones to map the favelas of Rio de Janerio.
The mappers physically travel around the favela and upload information on each individual landmark (restaurants, roads etc.) as they go. They use Nokia N95s mobile phones that are connected to Google Maps (http://www.maps.google.com). The project then uses Wikimapa (http://www.wikimapa.org.br), and Twitter (http://www.twitter.com) to log the information.
Published: October 2011
Resources
1) Zawarib Beirut Road Atlas: The Zawarib Beirut can be purchased from Amazon’s website. Website: http://www.amazon.co.uk/Zawarib-Beirut-Greater-Atlas/dp/9953005311
2) Google Maps: A treasure trove of global maps and data. Website: http://maps.google.co.uk/
3) Google Street View: A global database of photographs showing neighbourhoods and streets. Website: http://maps.google.com/intl/en/help/maps/streetview/#utm_campaign=en&utm_medium=van&utm_source=en-van-na-us-gns-svn
4) Google Maps for mobile: Use Google Maps on your phone, and never carry a paper map again. Website: http://www.google.co.uk/mobile/maps/

https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/02/17/digital-mapping-to-put-slums-on-the-map/
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.








https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/03/05/southern-innovator-issue-1/

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2022











You must be logged in to post a comment.