By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

In the Philippines, one animal’s call of nature has become a business opportunity.
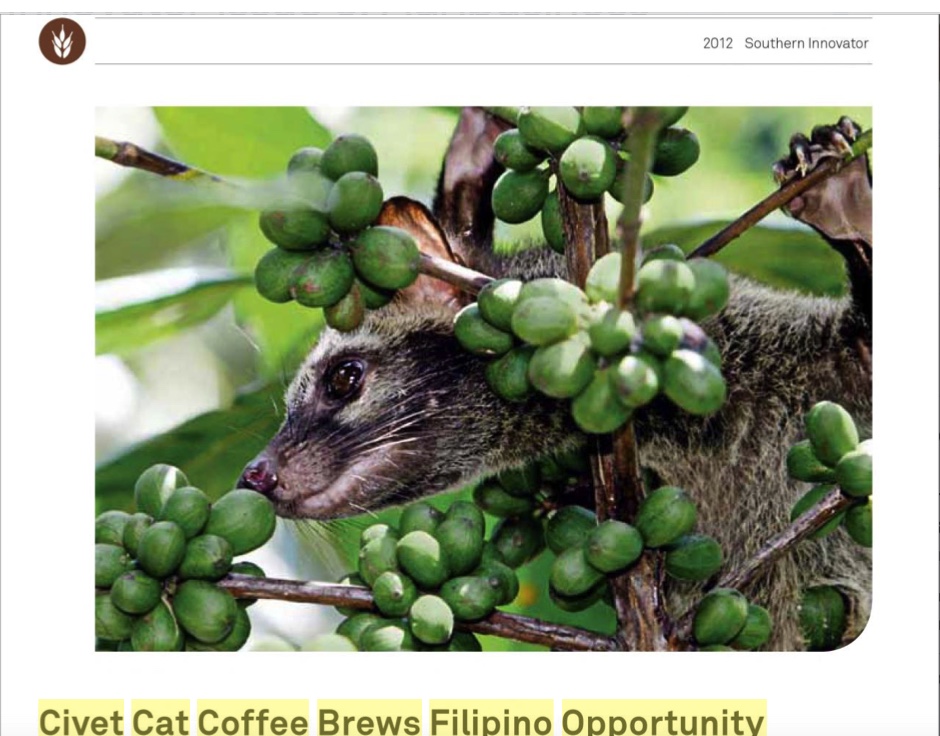
The civet cat, a member of the mongoose family, ingests the fruit of coffee plants, and expels the beans. This has created an unexpected by-product – a prized beverage for the world’s savvy coffee drinkers seeking the next taste sensation. The partially digested coffee beans are gathered from the faeces of the cat and used to make a much-coveted, smooth-flavoured cup of coffee.
It is a good example of how value can be added to a product, in this case coffee beans, producing a substantially higher income. The coffee is startlingly expensive: 50 grams cost US $70, 100 grams US $90, and 1 kilogram is a whopping US $870. The coffee is a blend of Arabica, Liberica and Exelsa beans, all of which have passed through the civet cats.
The highly prized coffee is driving a growing market for these rare beans around the world. But as demand rises, it becomes clear it is a market needing quality control and ethical practices.
One business that is trying to do this is Coffee Alamid (www.arengga.com), based in Las Pinas in the Philippines. It bills the coffee as the “World’s Rarest Brew. The Philippines’ Pride.”
Coffee Alamid’s founders, Basil and Vie Reyes, call themselves “coffee entrepreneurs” who started in the business from scratch.
“When we started Cafe Alamid, we were not even coffee drinkers,” they explain on the company’s website. “We didn’t know anything about coffee at all!”
Experienced in making Arengga vinegar (http://www.arengga.com/index.php/arengga-pinnata-its-not-just-a-vinegar.mpc), they discovered the civet cats that lived among the sugar palm trees used for making the vinegar. They did some research and were inspired by the Kopi Luwak, the Indonesian variety of civet cat coffee and wondered why they couldn’t do the same thing in the Philippines.
They consulted with the local forest-dwellers of Indang, Cavite and Batangas, who confirmed they gathered the civet cat droppings to make into coffee, part for personal consumption, with the rest sold in local markets. Gathering the civet droppings provides an income to the forest residents, who collect an average of one kilogram a day.
Some were sceptical of the idea: why bother with such a time-consuming product? But the Reyeses were inspired by the success of civet coffee in Indonesia and it inspired them to try it in the Philippines. They see themselves as “enlightened entrepreneurs” who believe in marrying business with social development.
The coffee is made from the wild civet cat droppings harvested from the forest floors of mountains in Malarayat, Lipa, Batangas and Mount Matutum, General Santos and South Cotabato in the Philippines. The beans are roasted and exported to Japan, Taiwan, Korea, Australia, the United States and Italy. The company produces between 1 and 1.5 tons of beans a year.
A proud moment for the business was becoming the first Filipino firm to participate in the Tea and Coffee World Cup in Geneva, Switzerland in 2007.
The brand’s name, Alamid, is the local name for the civet cat (Paradoxorus Philippinensis). It belongs to the mongoose family and forages for food at night, eating the ripest and sweetest coffee cherries during the coffee season.
By morning the civet cats excrete the undigested beans. While inside the cat’s stomach, enzymes and stomach acids go to work on the beans, altering their structure. The beans ‘ferment’ in the cat’s stomach, a process that has been analyzed by Dr. Massimo Marcone, a scientist from Canada’s University of Guelph.
Marcone traveled to Ethiopia and Indonesia in 2003 to collect the rare coffee beans. He found the beans’ taste – described as “earthy, musty, syrupy, smooth and rich with jungle and chocolate undertones” – was due to the lack of protein in the bean.
“The civet beans are lower in total protein, indicating that during digestion, proteins are being broken down and are also leaked out of the bean,” Marcone told the Luwak Kopi website. “Since proteins are what make coffee bitter during the roasting process, the lower levels of proteins decrease the bitterness of Kopi Luwak coffee.”
“Civet beans are typically extensively washed under running water after collection, which dislodges bacteria,” he said.
Marcone published his research into the beans in the paper “Composition and properties of Indonesian palm civet coffee (Kopi Luwak) and Ethiopian civet coffee.” (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0963996904001309)
The beans are greenish-brown when they come out in the cat faeces. Marcone found the process in the civet cat removes some of the caffeine, giving a strong cup of coffee less kick; this also makes the flavour smoother.
Supply is tight and this has led to some people forging the coffee or using unethical practices to get their hands on the beans. It is a business that needs to be run in an ethical way to ensure the rich profits are shared with everyone involved.
Marcone warns against imitations. “About 42 percent of all the kopi luwaks that are presently on sale are either adulterated or complete fakes, unfortunately,” he told the Los Angeles Times.
Coffee Alamid’s parent company, Bote Central, started as a family-owned company in 2002, with the idea of using agro-forestry products to create sustainable livelihoods and help preserve the environment. It wanted to introduce Fair Trade principles to the Philippines coffee industry.
Structurally, the company uses community roasting business units (CRBU) across the Philippines, in particular the countryside, to improve the way coffee is sold and make it more profitable for local economies. There are currently 12 such units, and more are planned. The company has put together a guide book on best practice for harvesting Arabica coffee beans based on their first-hand experience. It also explains how they maintain quality control (http://www.scribd.com/doc/19991462/Production-Guide-for-Arabica-Coffee-by-Bote-Central-Inc-Maker-of-Coffee-Alamid).
The company deals directly with farmers to avoid middlemen gouging profits, and tries to use technology to make the business more efficient and sustainable.
To keep quality improving, the company has also produced a manual on how to grow and harvest Arabica coffee beans. It is designed to tackle the practical realities of coffee production and show how to improve current methods to produce a better-quality bean. This is critical for the overall business as competition is fierce and quality has to constantly be improved.
Coffee Alamid has successfully positioned itself as a high-end, high-cost product. It is sold by Japan Airlines and by department stores in Japan and specialty coffee shops around the world.
Civet cat coffee continues to develop new fans. In Britain, the Birmingham-based Urban Coffee Company (http://www.urbancoffee.co.uk) has started selling the coffee.
‘It’s actually really nice,” sales manager Mark Bridgens told the Daily Mail newspaper. “It has a unique, soft taste. I’d definitely buy a cup of it, it’s very different.”
Published: June 2011
Resources
1)Fair Trade Foundation: Fairtrade is about better prices, decent working conditions, local sustainability, and fair terms of trade for farmers and workers in the developing world. Website: http://www.fairtrade.org.uk/
2) The red dot logo stands for belonging to the best in design and business. The red dot is an internationally recognized quality label for excellent design that is aimed at all those who would like to improve their business activities with the help of design. Website: http://www.red-dot.de
3) Small businesses looking to develop their brand can find plenty of free advice and resources here. Website: www.brandingstrategyinsider.com
4) Brandchannel: The world’s only online exchange about branding, packed with resources, debates and contacts to help businesses intelligently build their brand. Website: www.brandchannel.com
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.
Follow @SouthSouth1
Google Books: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=JIKYBgAAQBAJ&dq=development+challenges+june+2011&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/DavidSouth1/development-challengessouthsouthsolutionsjune2011issue
Southern Innovator Issue 1: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Q1O54YSE2BgC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 2: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ty0N969dcssC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 3: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=AQNt4YmhZagC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 4: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=9T_n2tA7l4EC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 5: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=6ILdAgAAQBAJ&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023







You must be logged in to post a comment.