By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

The tide of science and innovation from the South is grabbing the world’s attention. While the big giants of India, China and Brazil are well-established hubs of invention, it is the once-overlooked continent of Africa that is generating current excitement. The atmosphere can be equated to the flush of innovation in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, as inventors tackled the budding new technologies of the combustion engine, flight, electricity and radio waves. These days, it’s the challenges of development, rapid urbanization and finding ways to ‘hack’ (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hack_%28technology%29), like adapting existing technology such as mobile phones or bicycles to new purposes.
That previous period of invention had a spirit of pioneering and making-do, of dreams and adaptability triumphing over poverty, and it laid the path for many new companies to sprout up and create wealth and jobs for millions. At this August’s Maker Faire Africa gathering (http://makerfaireafrica.com/) in Accra, Ghana, African pioneers in grassroots innovation offered inspiring inventions.
The rapid changes happening in African countries – especially the tilt to having a larger urban population than a rural one – means there is an urgent need to boost incomes.
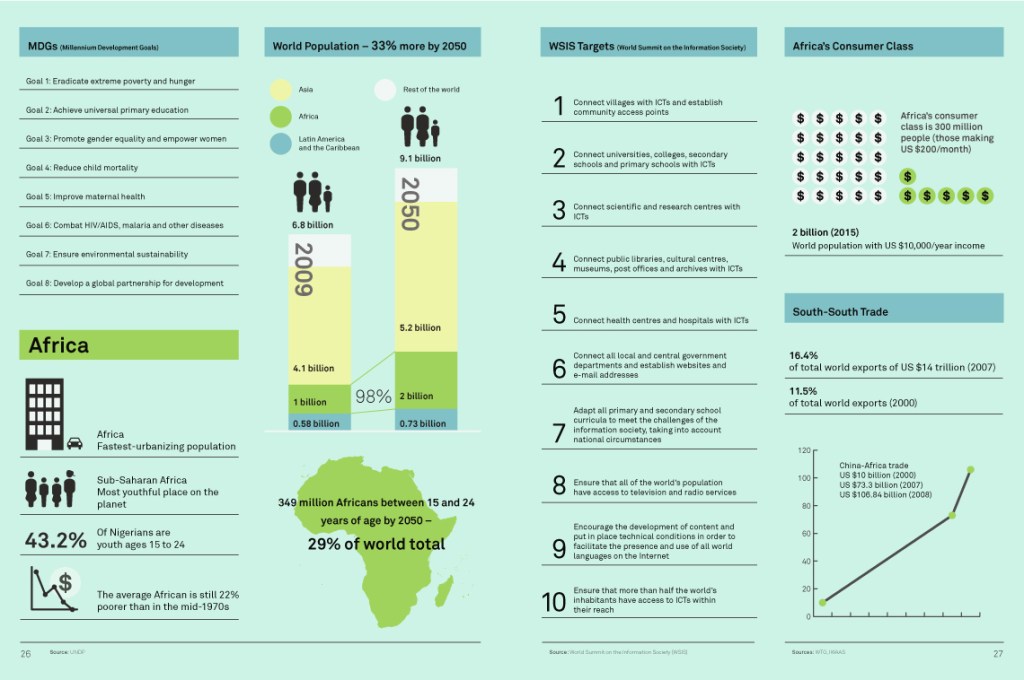
Handled right, these grassroots inventors could grow to become part of the already expanding South-South trade, which grew by an average of 13 percent per year between 1995 and 2007, to make up 20 percent of world trade.
Inspired by the US magazine Make (http://makezine.com/) – a do-it-yourself technology magazine written by makers of computers, electronics and robotics – the first Maker Faire gathering was held in 2006 in the San Francisco area of the United States.
The African Maker Faire modelled itself on this approach and has tapped into Africa’s well-entrenched do-it-yourself development culture. It went looking for more inventors like those celebrated on the website AfriGadget (http://www.afrigadget.com/), with its projects that solve “everyday problems with African ingenuity.” The Faire works with the participants to share their ideas and to find ways to make money from their ideas.
The Faire in Accra ran in parallel with the International Development Design Summit (http://2009.iddsummit.org/),which came to Ghana from its home at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (http://web.mit.edu/) in the United States. Its aim was to bring technology closer to “potential end users of the projects.”
“It is part of the revolution in design that aims to create equity in the distribution of research and development resources by focusing on the needs of the world’s poor,” organizers said.
This spirit of African invention is about breaking the perception that invention is a purely Northern phenomenon that requires complex and expensive materials. African ingenuity is about taking whatever is available and tackling common problems. It is an empowering approach that celebrates local initiative and seeks to find ways to turn these inventions into sustainable incomes.
“What’s different about African mechanics and gadgets is that it’s generally made with much fewer, and more basic, materials,” said Afrigadget founder Erik Hersman. “Where you might find a story on how to make hi-tech robots at home in Make, its counterpart in Africa might be how to create a bicycle out of wood. No less ingenuity needed, but far more useful for an African’s everyday life.”
The African Maker Faire featured a wide range of solutions, from a low-power radio station to a bicycle-powered saw and a simple corn planter.
Shamsudeen Napara, from northern Ghana, brought a US $10 corn planter that looks like a pill dispenser to help speed up crop planting. He also has invented a cheap shea nut (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shea_butter) roaster. These inventions are cooked up in his metal fabrication shop which builds tools for agricultural use. Shea nut processing is a lucrative task for women in Northern Ghana. Napara’s roaster costs US $40 and reduces the energy and time to process the nuts. He has also made a soap cutter using piano wires and guitar screws.
Bernard Kiwia, a bicycle mechanic from Arusha, Tanzania, is a pioneer working with windmills, water pumps, mobile phone chargers and pedal-powered hacksaws – all made from old bike parts.
Hayford Bempong, David Celestin and Michael Amankwanor from Accra Polytechnic (http://www.accrapolytechnic.edu.gh/), built a low-power radio station. Made from scrap electronic parts and an antenna from copper pipe, the radio was put straight to use to broadcast announcements at the event over a range of a few thousand metres.
Suprio Das, Killian Deku, Laura Stupin and Bernard Kiwia brought a method to produce chlorine from salt water and other common materials. It can then be used to purify water. Their method can clean vast quantities of water using no moving parts (avoiding breakdowns). It does this by dripping chlorine into the water until a level has been reached, and then the purified water is released. By using a 5 litre bag of chlorine, and a US $3 valve, 100,000 litres of water can be purified.
Electricity was also being made using low-cost batteries from aluminum cans and plastic water bottles. Applying salt water as an electrolyte (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrolyte),electricity is created by the oxidation of the aluminum can – a cheaper approach and less toxic than commercial batteries.
A group called Afrobotics (http://www.afrobotics.com) gave a presentation to encourage more African students to go into engineering, science and technology. Afrobotics is set up as a competition to “fuel engineering, science, innovation, and entrepreneurship on the African continent, utilizing robotics.” They have some excellent videos of African robots in action: http://www.afrobotics.com/videos.
Published: October 2009
Resources
1) Fab Labs: Like the futuristic “replicator” in the TV show Star Trek, Fab Labs allow people to design and produce what they need there and then. The labs are mushrooming throughout the South as people get the innovation bug. The Fab Lab program is part of the MIT’s Center for Bits and Atoms (CBA) which broadly explores how the content of information relates to its physical representation. Website: http://fab.cba.mit.edu/
2) id21 Insights: A series of articles by the UK ’s Institute of Development Studies on how to make technology and science relevant to the needs of the poor. Website: http://www.id21.org/insights/insights68/art00.html
3) eMachineShop: This remarkable service allows budding inventors to download free design software, design their invention, and then have it made in any quantity they wish and shipped to them: Amazing! Website: http://www.emachineshop.com/
4) The red dot logo stands for belonging to the best in design and business. The red dot is an internationally recognised quality label for excellent design that is aimed at all those who would like to improve their business activities with the help of design. Website: www.red-dot.de
5) Institute for the Future: It identifies emerging trends that will transform global society and the global marketplace. It provides insight into business strategy, design process, innovation, and social dilemmas. Its website helps budding inventors to identify new areas of invention.Website: http://www.iftf.org/

Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.





This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023










You must be logged in to post a comment.