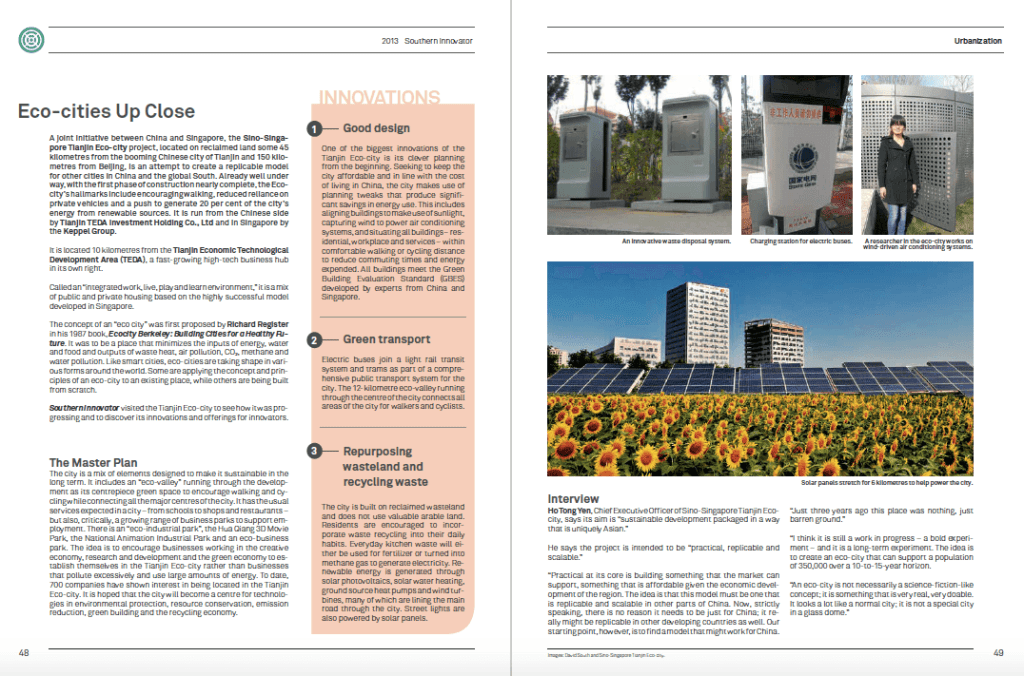
By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

China has a vast and growing market for the Internet and mobile devices. Over the past decade that market has been largely confined to China – most businesses have had enough domestic demand and opportunities inside the country to keep them busy.
But now companies in China’s dynamic Internet and mobile sector are seeking out new markets outside the country. Both online shopping service Alibaba (alibaba.com) and Weibo (weibo.com), the Chinese version of Twitter (twitter.com), are seeking to list on the New York Stock Exchange. The excitement this news has generated shows how many people want to get a piece of the large Chinese market for technology, social networks and online shopping. It is also sending a chill through America’s Silicon Valley – home to the country’s innovative high technology sector – that they are missing out on China’s fast-growing marketplace. Many American services are banned from operating in China. Even more worrying for Silicon Valley, these home-grown Chinese companies, with the market sewn up at home, are now set to compete globally for customers using their increasingly deep pockets.
One example is Tencent (http://www.tencent.com/en-us/index.shtml), owner of popular Chinese social messaging application (app) Weixin (weixin.qq.com), known as WeChat (wechat.com) outside China. Used on mobile phones and smartphones, Weixin has gained 300 million users in just three years, becoming the dominant social messaging service in the world’s largest smartphone market. Its has been so successful that many rivals are trying to chip away at its customer base.
Weixin, pronounced way-shin, allows smartphone users to send messages and share news, photos, videos and web links with friends. One of its selling points is its claim to not store messages on its servers.
Building on its success in social networking in China, it is looking to expand in other markets, including Southeast Asia, Europe and Latin America. It also wants to grow its offerings in online payment and e-commerce.
One factor in Weixin’s success is the ability to send messages by recording a voice message rather than just typing in characters: very useful for non-Latin script users, and especially for Chinese-language users, who use thousands of characters in everyday communication.
One ambitious forecast claims Weixin could reach 400 million users and make US $500 million revenue within a year.
Cosmetics marketer Jenny Zhao, who uses an iPhone 5, told The New York Times: “I’m probably on Weixin six hours a day. A lot of what I do revolves around it.”
“I use Weixin every day,” said Zhang Shoufeng, a food and drinks seller. “My friends are on it and my boss is on it. We are talking about where to eat, where to hang out and where to meet for company conferences. This is how we communicate.”
Analysts believe Weixin has benefitted from not having to compete with banned-in-China American company Facebook (facebook.com).
“Even if Facebook had permission, it’s probably too late,” said Wang Xiaofeng, an analyst at Forrester Research. “Weixin has all the functionality of Facebook and Twitter, and Chinese have already gotten used to it.”
Tencent is an example of a wider trend: As Chinese companies and offerings have become stronger, wealthier and more innovative, they increasingly look to build their customer base outside China.
Founded in November, 1998, Tencent, Inc. has grown into China’s largest and most used Internet service portal. Its most popular services include QQ (QQ Instant Messenger), WeChat, QQ.com, QQ Games, Qzone, 3g.QQ.com, SoSo, PaiPai and Tenpay, as well as Weixin.
The company claims to put innovation at the heart of its business, with more than half of its employees devoted to research and development. The Tencent Research Institute, established in 2007 with RMB 100 million (US $16 million), calls itself “China’s first Internet research institute, with campuses in Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen.” It has patents for technologies it has developed for instant messaging, e-commerce, online payment services, search, information security, and gaming.
Tencent was driven to innovate by a fear it could quickly become irrelevant in the information technology space. Weixin is also pioneering ways to book taxis, hotels and airline flights through the service and even ways to control home appliances.
“Chinese Internet companies are no longer behind,” said William Bao Bean, a managing director at the venture capital firm SingTel Innov8 (http://innov8.singtel.com/). “Now in some areas, they’re leading the way.”
Published: April 2014
Resources
1) Weibo: Sina Weibo is a Chinese microblogging (weibo) website. Akin to a hybrid of Twitter and Facebook, it is one of the most popular sites in China, in use by well over 30 per cent of Internet users, with a market penetration similar to what Twitter has established in the USA. Website: weibo.com
2) Laiwang: A variation on the WeChat service, its biggest competitor. Website: laiwang.com
3) WhatsApp: WhatsApp Messenger is a cross-platform mobile messaging app which allows you to exchange messages without having to pay for SMS. Website: whatsapp.com
4) Southern Innovator Issue 1: Mobile Phones and Information Technology: Pioneering and innovative ways to deploy mobile phones and information technology to tackle poverty. Website: http://www.scribd.com/doc/57980406/Southern-Innovator-Magazine-Issue-1 and here: http://tinyurl.com/q6bfnpz
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/10/20/china-consumer-market-asian-perspective-helps/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2021/01/26/designed-in-china-to-rival-made-in-china/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2020/04/17/virtual-supermarket-shopping-takes-off-in-china/
Citation


Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP’s South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South’s innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2025














You must be logged in to post a comment.