By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

Information technology developments in Africa have long lagged behind those in other parts of the world. But the transformation being brought about by the widespread adoption and use of mobile phones – each one a mini-computer – and the expansion of undersea fibre optic cable connections to Africa are creating the conditions for an exciting new phase of computing growth on the continent.
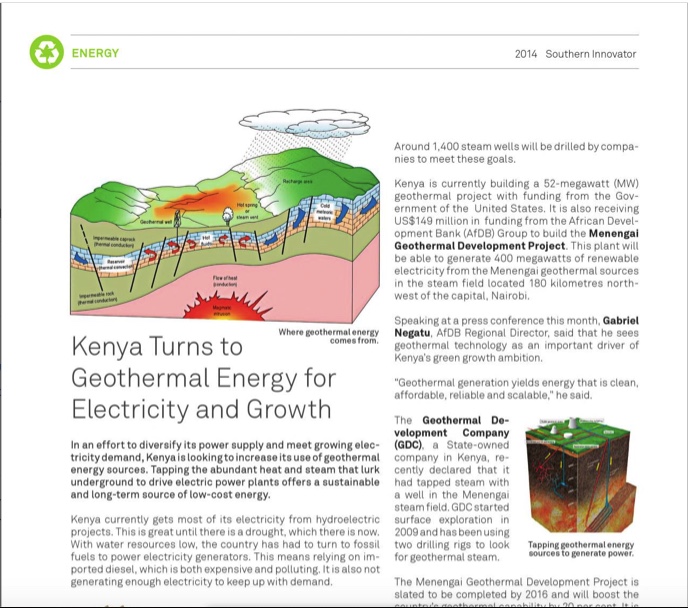
Despite the global economic crisis, Africa is on course to see annual consumer spending reach US $1.4 trillion by 2020, nearly double the US $860 billion in 2008 (McKinsey). On top of this, by 2050, a projected 63 per cent of Africa’s population will be urban dwellers. With Africa’s middle class the fastest-growing in the world – doubling in less than 20 years – matching computing power with this consuming urban population could unleash a treasure trove of opportunity for information technology entrepreneurs.
These developments are creating the conditions for game-changing computing in the next years. And this is encouraging the creation of a new supercomputer (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supercomputer) for Africa in Kenya that will double the total number of supercomputers in Africa. Hugely powerful compared to personal or commercial computers, supercomputers use cutting-edge technology to carry out high-speed calculations involving vast quantities of data.
Expanded supercomputing power brings numerous advantages to both economic and human development. It will radically alter what can be accomplished in Africa – allowing mass data processing to be done, highly complex and data dense applications to be run, and very large research projects to be conducted on the continent rather than overseas.
Increasing computing power in Africa will bring in its wake, it is hoped, a surge in economic and research opportunities.
It will help African researchers and scientists to undertake globally competitive projects, rather than seeing this work done overseas. It will also open up a vast range of possibilities for African entrepreneurs and businesses to do complex data processing, modelling and research and will enable them to become more sophisticated operations.
The new supercomputer, the iHub Cluster, is being built in the Kenyan capital by one of Africa’s pioneering information technology hubs – iHub Nairobi (http://ihub.co.ke/pages/home.php) – in partnership with Internet products and services company Google and microchip maker Intel Corporation.
Africa’s first supercomputer is located in South Africa and is ranked 497 in terms of computing power on the list of 500 supercomputers in the world (http://www.top500.org/).
It is located in the “Tsessebe cluster” in Cape Town’s Centre for High Performance Computing (http://www.chpc.ac.za/).
“With mobile devices coming in multiple cores, it is important for developers to be exposed to higher performance computing; we are hoping to debut at a higher level than ‘Tsessebe cluster’,” Jimmy Gitonga, the project team leader for the iHub cluster, told Computer World.
Africa suffers from poor supercomputer capacity and this has had a knock-on affect on everything to do with economic development. The iHub supercomputer hopes to help universities and colleges to gain competitive edge and be able to undertake more complex research in the fields of media, pharmaceuticals and biomedical engineering.
“In Africa, we need to be on top of the mobile scene, its our widest used device,” Gitonga told Computer World.
Some of the practical applications for the iHub supercomputer in East Africa and the Horn of Africa include improving weather forecasting and drought prediction, increasing the ability to give advance warning of droughts and famines in the region.
“Most of the United Nations agencies and international agencies operating in the region have extensive field research on how to tackle natural disasters in the region. Imagine if they had affordable space where they can meet with developers and test resource-hungry applications,” Gitonga said.
The iHub also wants to offer the services of the supercomputer to researchers and organizations who have had to go abroad to have their data processed.
The iHub supercomputer hopes to be used by mobile phone developers, gamers, universities and research institutions.
In the last two years, China had pushed the United States out of the number one spot for supercomputers. The Tianhe-1A located at the National Supercomputing Center in Tianjin (http://www.nscc-tj.gov.cn/en/), China, was the fastest computer in the world from October 2010 to June 2011.
For those looking to see how they can make the most of the growing supercomputer capability in Africa, examples from other countries offer a good idea. Supercomputers can be used for weather forecasting, climate research, oil and gas exploration, physical simulations like when testing aircraft, complex modelling for medical research, processing complex social data necessary for delivering effective social programmes or running modern health care systems.
Published: October 2012
Resources
1) A video on how to use a supercomputer. Website:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yvbSX–LOko
2) Southern Innovator Issue 1: Mobile Phones and Information Technology. Website:http://www.scribd.com/doc/95410448/Southern-Innovator-Magazine-Issue-1-Mobile-Phones-and-Information-Technology?in_collection=3643685
3) Read more about the iHub supercomputer. Website:http://www.ihub.co.ke/blog/2012/09/the-ihub-cluster/
4) More on High Performance Computing from Intel Corporation. Website:http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/high-performance-computing/server-reliability.html
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/11/african-breakthroughs-to-make-life-better/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/20/african-bus-to-tackle-african-roads/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/19/african-culture-as-big-business/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/17/african-ingenuity-attracting-interest/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/15/african-innovators-celebrated-in-prize/
https://davidsouthconsulting.org/2022/11/02/african-online-supermarket-set-to-boost-trade/

Like our content? Help contribute to the costs of keeping it online.


This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2021










You must be logged in to post a comment.