By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions

The developing world’s rapidly growing cities are bringing with them whole new ways of living and working. One rapidly expanding category of citizen is the office worker. A symbol of growing prosperity, the office worker also tends to be a time-poor person who often must commute large distances between home and workplace.
These long commutes mean that many workers have lost the old ability to go home for lunch. This has led to an expanding new field of business: catering to all these office workers’ appetites.
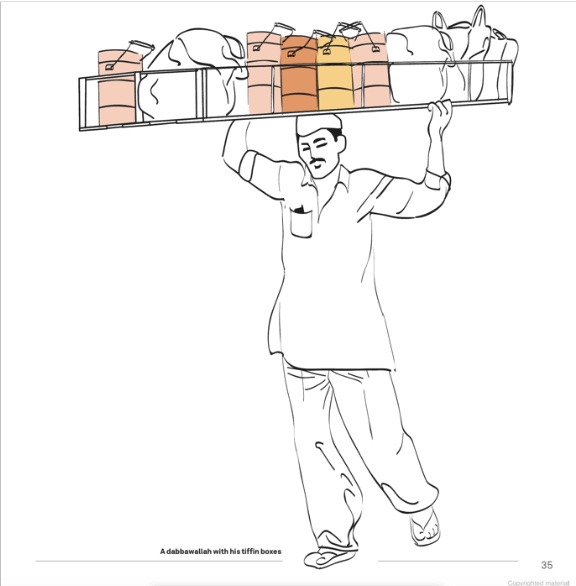
Every morning Mumbai’s legendary dabbawallahs (it means “box-carrier” or “lunchpail man”) fan out across the city to collect freshly prepared lunches from people’s homes and restaurants. They then efficiently use the transport network to quickly deliver lunches to the customers’ workplaces. Once just for the elite, the dabbawallah lunch has become the norm for Mumbai’s middle class office workers. Lunches are packed into small, metal tiffin boxes, ingeniously organized so each component of the meal is sealed in its own section and kept warm.
With a plethora of religious and cultural practices, Indians are particular about what they eat. In Mumbai there are 200,000 office workers receiving cooked lunches every day delivered straight to their desks. This is done by an army of 5,000 dabbawallahs. While their delivery accuracy was already impressive – only six deliveries in a million go astray – they realized they had to adapt to the city’s rapid changes. In addition to their network using trains, hand-carts and bicycles to get the lunches to desks, they have turned to the internet and mobile phone SMS text messaging to take orders.
It is a 125-year old industry that has grown at the rate of five to ten per cent a year and all are paid the same no matter what their function in the business.
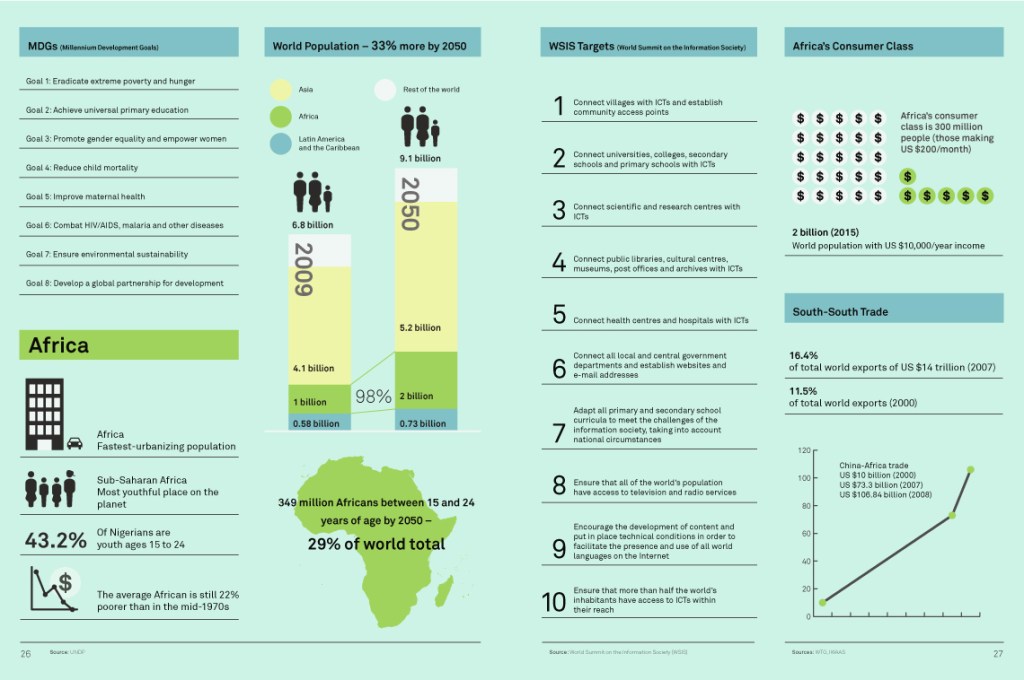
With foreign direct investment into developing countries surging – according to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), it rose by 12 per cent from 2005 to 2006 – the number of office workers is on the rise too.
The trend is especially pronounced in India, which is on track to overtake the United Kingdom as the world’s fifth largest economy by 2010, according to investment bankers Goldman Sachs.
India’s cities are booming. Mumbai is one of the top five global megacities as well as the world’s most crowded metropolis. The dabbawallahs are an excellent example of how a business can move with the times.
A key component in India’s new-found success has been a willingness to do things better and become more efficient; the key to this is often information technology. The new technology for the dabbawllahs has been built for them by software engineer Manish Tripathi – he has even been adopted as an honorary tiffinwallah.
“When people move to Mumbai for work, and need a lunchbox carrier, who do they ask?” he said. “They ask their friends, or their neighbour. Now, they just need to go to the website and they can find out how to get in touch with us. They can also get in touch with us via SMS.”
The move online has been a great success said Tripathi: “We get 10 to 15 enquiries more a day via SMS and the website.”
Raghunath Medge from the dabbawallahs cooperative said they are also making money by selling advertising on table mats. They have also turned to being a health service: they distribute health advice, beginning with this year’s World AIDS Day. An “AIDS kit”, comprising a car calendar and fliers on testing and counselling tied neatly with a red ribbon, was distributed ahead of World AIDS Day December 1.
“The kit was attached to empty lunch boxes and delivered to about 100,000 clients’ homes,” said Raghunath Megde,
Targeting hungry office workers is a goldmine for others too: in Saigon, Vietnam, the Ben Thann restaurant capitalised on its proximity to an area with a fast-growing office worker population to increase its profits. “Since our restaurant began serving lunch for office workers our business has increased by 60 per cent. This increase in number of guests enjoying the new menu was the main reason for Ben Thanh’s decision to introduce a buffet lunch,” said Nguyen Thi Thu Thao, deputy manager of Ben Thanh Restaurant.
In the past, the dabbawallahs were visited by Prince Charles and British entrepreneur multimillionaire Richard Branson, to study their working methods. It looks like this next round of innovation will equally grab the world’s attention.
Published: December 2007
Resources
- The New York Times has an excellent slideshow of the dabbawallahs at work: Click here to view
- The official website of the dabbawallahs: http://www.mydabbawala.com/






“I think you [David South] and the designer [Solveig Rolfsdottir] do great work and I enjoy Southern Innovator very much!”
Ines Tofalo, Programme Specialist, United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052.
© David South Consulting 2023












You must be logged in to post a comment.